Namestite Plesk na CentOS 7
Uporaba drugega sistema? Plesk je lastniška nadzorna plošča spletnega gostitelja, ki uporabnikom omogoča upravljanje svojih osebnih in/ali strank spletnih mest, baz podatkov
H2O je HTTP strežnik nove generacije, ki ima odlično, popolnoma opremljeno HTTP/2 implementacijo vseh trenutnih spletnih strežnikov v uporabi. S H2O kot spletnim strežnikom lahko izkoristite prednosti novih funkcij specifikacije HTTP/2, kot so optimizacija zakasnitve, potiskanje strežnika in določanje prednosti na strani strežnika, ki lahko izkoristijo prednosti sodobnih funkcij brskalnika, o katerih se redko govori.
V tej podrobni vadnici vam bom korak za korakom pokazal, kako zagnati H2O, da deluje na vašem CentOS 7 x64 primerku.
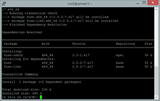
Prijavite se prek SSH s poverilnicami, ki jih najdete pod vašim primerkom, in posodobite sistem, kot sledi.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
Če želite namestiti H2O na CentOS 7, morate dodati repozitorij Bintray RPM za namestitev vnaprej vgrajenih binarnih datotek H2O. Z urejevalnikom Nano ustvarite repo po meri.
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-h2o-rpm.repo
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v repo datoteko.
[bintray-h2o-rpm]
name=bintray-h2o-rpm
baseurl=https://dl.bintray.com/tatsushid/h2o-rpm/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Nato namestite H2O.
sudo yum install h2o -y
Zdaj, ko je H2O nameščen, toda preden omogočite in zaženete storitev, je potrebna ustrezna konfiguracija in ustvariti moramo določenega uporabnika in skupino, pod katero bo H2O deloval. Ustvarite skupino in uporabnika za H2O, ki se bo izvajal pod named h2o.
sudo groupadd -g 101 h2o
sudo useradd -d /etc/h2o -g 101 -M -s /sbin/nologin -u 101 h2o
Naslednji koraki bodo podali primere konfiguracijskih nastavitev za različne nastavitve unencrypted, encrypted, staticin dynamicstrežnika; kot tudi kombinacija vseh štirih.
http://www.example.comna http://example.com(statične strani HTML, brez PHP) konfiguracijoPomaknite se do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte privzeto h2o.confv h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Ustvarite novo h2o.confdatoteko.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v h2o.confdatoteko.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Omogočite in zaženite strežnik H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Ustvarite privzeto index.htmls predlogo v /var/www/htmlmožnosti imenika, ki je file.dirnavedena zgoraj v /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Zdaj odprite brskalnik in vnesite ime domene strežnika ( example.comali www.example.com) za vaš primer. Dobiš sporočilo Unable to connectali This site can’t be reachedsporočilo? Privzeta nastavitev požarnega zidu CentOS onemogoča dohodne povezave na vrata http. Izvedite naslednje, da ga odprete.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvežite stran v brskalniku ( F5) in prejeli boste to sporočilo.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.comna http://www.example.com(statične strani HTML, brez PHP) konfiguracijoPomaknite se do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte privzeto h2o.confv h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Ustvarite novo h2o.confdatoteko.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite naslednje besedilo v h2o.confdatoteko.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Omogočite in zaženite strežnik H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Ustvarite privzeto index.htmldatoteko s predlogo v /var/www/htmlmožnosti imenika, ki je file.dirnavedena zgoraj v /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Zdaj odprite brskalnik in vnesite ime domene strežnika ( example.comali www.example.com) za vaš primer. Dobiš sporočilo Unable to connectali This site can’t be reachedsporočilo? Privzeta nastavitev požarnega zidu CentOS onemogoča dohodne povezave na vrata http. Če ga želite odpreti, naredite naslednje.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvežite stran v brskalniku ( F5) in prejeli boste to sporočilo.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://www.example.comna http://example.com(Dinamična stran, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) konfiguracijoPomaknite se do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte privzeto h2o.confv h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Ustvarite novo h2o.confdatoteko.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite naslednje besedilo v h2o.confdatoteko.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://www.example.com To http://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text into the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, in https://example.comna https://www.example.com(Dinamična stran, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) konfiguracijaPomaknite se do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte privzeto h2o.confv h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Ustvarite novo h2o.confdatoteko.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v h2o.confdatoteko.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Ustvarite imenik po meri za shranjevanje privzetih možnosti SSL za vsa spletna mesta, ki uporabljajo SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Ustvarite novo ssl.confdatoteko.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v ssl.confdatoteko.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Ustvarite imenik za shranjevanje dhparam_2048.pemdatoteke, ki se bo dnevno regenerirala prek cronjoba.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Ustvarite novo regenerate_dhparamdatoteko.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Kopirajte in prilepite naslednje besedilo v regenerate_dhparamdatoteko.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Naj bo pravkar ustvarjena datoteka bash izvedljiva.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Izvedite skript bash za prvi zagon, saj se H2O ne bo pravilno zagnal, če ni ustvarjen. To bo trajalo približno minuto ali dve, da se ustvari ob prvem zagonu.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Za obdelavo PHP mora biti nameščen in konfiguriran demon PHP-FPM 7.1. Če želite namestiti različico PHP-FPM, novejšo od privzete 5.4.x, mora biti nameščen repo REMI, ki vsebuje različice PHP 5.6.x, 7.0.x in 7.1.x. Vnesite naslednje ukaze za namestitev PHP različice 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Pomaknite se do /etc/opt/remi/php71/imenika.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Preimenujte privzeto php-fpm.confv php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Ustvarite novo php-fpm.confdatoteko.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite naslednje besedilo v php-fpm.confdatoteko.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Preimenujte privzeto www.confdatoteko v php-fpm.dimeniku.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Ustvarite novo www.confdatoteko.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v www.confdatoteko. Spremenite svoj tako, pm.max\_childrenda bo ustrezal številu CPE-jev v skladu z vašim primerkom VPS.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Preimenujte privzeto php.inidatoteko.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Ustvarite novo php.inidatoteko.
sudo nano php.ini
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v novo php.ini file. Spremenite memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesizein date.timezonev skladu s svojim primerkom VPS.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Spremenite lastništvo skupine za /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/imenik iz apacheskupine v h2oskupino.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Ustvarite imenik, kjer bodo shranjeni dnevniki strežnika PHP-FPM.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Omogočite in zaženite strežnik PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Omogočite in zaženite strežnik H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Ustvarite imenik, v katerem bo privzeta vrednost, index.phpnavedena v file.dirzgornji možnosti imenika v /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Ustvarite privzeto index.phpz phpinfoukazom za testiranje PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Kopirajte in prilepite spodnje besedilo v novo index.phpdatoteko.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Zdaj odprite brskalnik in vnesite ime domene strežnika ( example.comali www.example.com) za vaš primer. Dobiš sporočilo Unable to connectali This site can’t be reachedsporočilo? Privzeta nastavitev požarnega zidu CentOS onemogoča dohodne povezave na vrata http. Če ga želite odpreti, naredite naslednje.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvežite stran v brskalniku ( F5) in dobili boste standardno stran z informacijami o PHP.
S tem zaključujem mojo vadnico. Hvala za branje.
Uporaba drugega sistema? Plesk je lastniška nadzorna plošča spletnega gostitelja, ki uporabnikom omogoča upravljanje svojih osebnih in/ali strank spletnih mest, baz podatkov
Squid je priljubljen brezplačen program za Linux, ki vam omogoča ustvarjanje spletnega proxyja za posredovanje. V tem priročniku boste videli, kako namestiti Squid na CentOS, da vas obrne
Uvod Lighttpd je razdelek Apache, katerega namen je biti veliko manj intenziven vir. Je lahek, od tod tudi njegovo ime, in je precej preprost za uporabo. Namestite
VULTR je pred kratkim naredil spremembe na svoji strani in zdaj bi moralo vse delovati v redu iz škatle z omogočenim NetworkManagerjem. Če želite onemogočiti
Icinga2 je zmogljiv sistem za spremljanje in če se uporablja v modelu glavni-odjemalec, lahko nadomesti potrebo po nadzornih pregledih, ki temeljijo na NRPE. Glavni naročnik
Uporaba drugega sistema? Apache Cassandra je brezplačen in odprtokodni sistem za upravljanje baz podatkov NoSQL, ki je zasnovan tako, da zagotavlja razširljivost, visoko
Uporaba drugega sistema? Microweber je odprtokodna povleci in spusti CMS in spletna trgovina. Izvorna koda Microweber gostuje na GitHubu. Ta vodnik vam bo pokazal
Uporaba drugega sistema? Mattermost je odprtokodna alternativa sporočilni storitvi Slack SAAS, ki jo gosti sami. Z drugimi besedami, z Mattermostom si pribl
Kaj potrebujete Vultr VPS z vsaj 1 GB RAM-a. SSH dostop (z root/administrativnimi pravicami). 1. korak: Namestitev BungeeCord Najprej najprej
Nadzorna plošča Plesk ima zelo lepo integracijo za Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt je eden edinih ponudnikov SSL, ki izdaja potrdila v celoti
V času pisanja je MariaDB 10.1 razvojna različica MariaDB. Temelji na MariaDB 5.5 in vključuje funkcije, prenesene nazaj iz MySQL 5.6. Ther
Lets Encrypt je certifikacijski organ, ki je namenjen brezplačnemu zagotavljanju certifikatov SSL. cPanel je zgradil lepo integracijo za vas in vašo stranko
Uporaba drugega sistema? Concrete5 je odprtokodni CMS, ki ponuja številne značilne in uporabne funkcije za pomoč urednikom pri preprosti izdelavi vsebine.
Uporaba drugega sistema? Review Board je brezplačno in odprtokodno orodje za pregledovanje izvorne kode, dokumentacije, slik in še veliko več. Gre za spletno programsko opremo
V tem priročniku se boste naučili, kako nastaviti preverjanje pristnosti HTTP za spletni strežnik Nginx, ki deluje na CentOS 7. Zahteve Za začetek boste potrebovali
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) je odprtokodna aplikacija za krajšanje URL-jev in analitiko podatkov. V tem članku bomo obravnavali postopek namestitve
Uporaba drugega sistema? Uvod ArangoDB je odprtokodna baza podatkov NoSQL s prilagodljivim podatkovnim modelom za dokumente, grafe in ključe-vrednosti. je
Uvod Imenik /etc/ igra ključno vlogo pri delovanju sistema Linux. Razlog za to je skoraj vsaka sistemska konfiguracija
Številni sistemski skrbniki upravljajo velike količine strežnikov. Ko je treba do datotek dostopati prek različnih strežnikov, se prijavite v vsakega posebej ca
Ta vadnica bo obravnavala postopek namestitve igralnega strežnika Half Life 2 na sistem CentOS 6. 1. korak: Namestitev predpogojev Za nastavitev ou
Umetna inteligenca ni v prihodnosti, tukaj je prav v sedanjosti. V tem blogu preberite, kako so aplikacije umetne inteligence vplivale na različne sektorje.
Ste tudi vi žrtev DDOS napadov in ste zmedeni glede načinov preprečevanja? Preberite ta članek, če želite rešiti svoja vprašanja.
Morda ste že slišali, da hekerji zaslužijo veliko denarja, a ste se kdaj vprašali, kako zaslužijo takšen denar? razpravljajmo.
Ali želite videti revolucionarne izume Googla in kako so ti izumi danes spremenili življenje vsakega človeka? Nato preberite v blogu in si oglejte Googlove izume.
Koncept samovozečih avtomobilov, ki zapeljejo na ceste s pomočjo umetne inteligence, so sanje, ki jih imamo že nekaj časa. A kljub številnim obljubam jih ni nikjer. Preberite ta blog, če želite izvedeti več…
Ker se znanost hitro razvija in prevzame veliko naših prizadevanj, se povečuje tudi tveganje, da se podvržemo nerazložljivi singularnosti. Preberite, kaj bi za nas lahko pomenila singularnost.
Metode shranjevanja podatkov so se lahko razvijale od rojstva podatkov. Ta blog pokriva razvoj shranjevanja podatkov na podlagi infografike.
Preberite blog, če želite na najpreprostejši način spoznati različne plasti v arhitekturi velikih podatkov in njihove funkcionalnosti.
V tem digitalno vodenem svetu so pametne naprave za dom postale ključni del življenja. Tukaj je nekaj neverjetnih prednosti pametnih naprav za dom o tem, kako naredijo naše življenje vredno življenja in poenostavijo.
Pred kratkim je Apple izdal macOS Catalina 10.15.4 dopolnilno posodobitev za odpravo težav, vendar se zdi, da posodobitev povzroča več težav, ki vodijo do opečenja računalnikov Mac. Preberite ta članek, če želite izvedeti več