Installer Plesk på CentOS 7
Bruker du et annet system? Plesk er et proprietært kontrollpanel for webverten som lar brukere administrere sine personlige og/eller klienters nettsteder, databaser
LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) er et av de forskjellige diskkrypteringsformatene som er tilgjengelige for Linux som er plattformagnostiske. Denne opplæringen vil gi deg rot- og byttepartisjoner inne i et LVM (Linux Volume Manager)-volum inne i en kryptert LUKS-partisjon. Denne opplæringen lar deg også låse opp LUKS-partisjonen eksternt ved å bruke en forenklet SSH-serverdemon ved å bruke et hvilket som helst kompatibelt SSH-klientprogram.
På siden Distribuer servere gjør du følgende:
Server Locationseksjonen.CentOS7under ISO Libraryfanen i Server Typeseksjonen.Server Sizedelen.Deploy Nowknappen.Bruk View Consolealternativet for å få tilgang til VPS-forekomsten via noVNC-konsollen.
Velg Install CentOS Linux 7alternativet.
Trykk på Tabtasten.
Gå inn textetter vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quietslik at det ser slik ut vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet textog trykk på Entertasten.
VPS vil nå starte opp i tekstmodus CentOS-installasjonsprogrammet. Du vil se en skjerm i noVNC-konsollen som vist på bildet nedenfor.

Bruk Alt + Right Arrow Keykombinasjonen for å navigere til TTY2-konsollen for å skrive kommandoer på kommandolinjen.
Skriv inn følgende kommandoer nedenfor for å lage en partisjon som inneholder GRUB2-oppstartslasteren, en ukryptert /bootpartisjon og en primærpartisjon som vil inneholde LUKS-partisjonen.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Skriv inn følgende kommando for å vise partisjonsoppsettet.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Deretter fyller du den navngitte rootfspartisjonen med pseudo-tilfeldige data. Dette vil ta litt over en halv time å fullføre.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
På CentOS 7 cryptsetupbruker kommandoene standard chiffer av aes-xts-plain64, standard nøkkelstørrelse på 256 biter og standard hash av SHA1. I stedet vil LUKS-partisjonen bli opprettet med det sikrere Serpent-chifferet, med en nøkkelstørrelse på 512 biter og med Whirlpool-hashen.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Skriv inn svarene når du blir bedt om det med følgende spørsmål, og trykk deretter på Entertasten:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordAdvarsel Dette vil tillate root-pålogging og kopiering uten passordforespørsel. Drep denne SSH-serveren etter at du har hentet /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfilen.
For sikker oppbevaring, lagre en kopi av LUKS-partisjonsoverskriften. Dette sikrer at hvis overskriften på LUKS-partisjonen din på en eller annen måte er skadet, kan den gjenopprettes. Hvis overskriften er skadet uten en fungerende sikkerhetskopi, går dataene dine tapt for alltid.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
For å kopiere /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfilen fra serveren, må en SSH-server startes midlertidig ved å bruke den sikre kopien scppå en klientvert for å hente den.
Skriv inn følgende kommando nedenfor for å generere SSH-vertsnøklene.
sshd-keygen
Skriv inn følgende kommando nedenfor for å lage /etc/ssh/sshd_configfilen.
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Skriv inn følgende kommando nedenfor for å redigere /etc/ssh/sshd_configfilen.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
For å redigere filen, trykk på Inserttasten og bruk piltastene til å navigere til deler av filen som må redigeres.
På linje én endrer du tallet Port 22fra standardverdien til 22til et tilfeldig antall du velger mellom 1025og 65535. (Eksempel: port 25782)
Rull ned til linje nummer tretten, trykk på Endtasten og trykk på Entertasten.
På neste linje legger du til HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_keyog trykker på Entertasten.
På neste linje legger du til HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keyog trykker på Entertasten.
Trykk på Esctasten, skriv :wqog trykk på Entertasten for å lagre filen.
Standard nettverksgrensesnitt eth0trenger en IP-adresse. Skriv inn følgende kommando nedenfor for å tilordne IP-adressen som er oppført for din instans til eth0nettverksgrensesnittet.
dhclient
Skriv inn følgende kommando for å vise den tildelte IP-adressen. IP-adressen vil bli oppført umiddelbart etter inetog før netmask. (Eksempel: inet 192.0.2.1nettmaske)
ifconfig eth0
Skriv inn følgende kommando for å starte SSH-serveren.
/usr/sbin/sshd
Hvis du bruker scpkommandoen fra en kommandolinje på en klientmaskin, bruk følgende kommando nedenfor som en mal for å hente /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfilen. Erstatt 25782med det faktiske portnummeret som er tildelt i /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Erstatt 192.0.2.1med den faktisk tildelte IP-adressen.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
Etter henting av luks-header-backup.imgfilen, drep SSH-serveren umiddelbart ved å skrive kommandoen nedenfor i noVNC-konsollvinduet.
killall sshd
Åpne LUKS-partisjonen for å sette opp det fysiske LVM-volumet som skal ligge inne.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Input the passphrase created earlier to open the LUKS partition when prompted, then press the Enter key.
Enter passphrase for /dev/vda3: strong-password
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named centos, control, live-base and live-rw. The centos is the LUKS partition.
Type the following command below to create the LVM physical volume.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Type the following command below to create the LVM volume group.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for a swap partition. Use sound judgment to create a swap partition, of the necessary size (-L = size of the volume), based on your VPS instance.
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "swap" created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for the root partition. This will use the remaining free space while reserving five percent (5%) to contain LVM snapshots of your logical volumes if you so choose.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "root" created
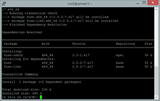
Display the LVM physical volume.
pvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM volume group.
vgdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM logical volume(s).
lvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Type the following command below to deactivate the LVM volume group. This must be completed in order to allow cryptsetup to close the LUKS partition in the next step.
vgchange -a n
When successful, you will receive the following message:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Close the LUKS volume.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
På klientsystemene dine, se seksjoner 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelyog 3.4. Unlocking using thelås commandopp Dracut-Crypt-SSH GitHub-siden for enten å tvinge frem en passordfrasemelding eller bruke unlockkommandoen til å åpne LUKS-partisjonen fra SSH-klienten din.
Bruker du et annet system? Plesk er et proprietært kontrollpanel for webverten som lar brukere administrere sine personlige og/eller klienters nettsteder, databaser
Squid er et populært, gratis Linux-program som lar deg lage en webproxy for videresending. I denne veiledningen vil du se hvordan du installerer Squid på CentOS for å gjøre deg om
Introduksjon Lighttpd er en apachegaffel som har som mål å være mye mindre ressurskrevende. Den er lett, derav navnet, og er ganske enkel å bruke. Installer
VULTR har nylig gjort endringer på sin side, og alt skal nå fungere bra ut av boksen med NetworkManager aktivert. Skulle du ønske å deaktivere
Icinga2 er et kraftig overvåkingssystem, og når det brukes i en master-klient-modell, kan det erstatte behovet for NRPE-baserte overvåkingskontroller. Mester-klienten
Bruker du et annet system? Apache Cassandra er et gratis og åpen kildekode NoSQL-databasebehandlingssystem som er designet for å gi skalerbarhet, høy
Bruker du et annet system? Microweber er en åpen kildekode dra og slipp CMS og nettbutikk. Microweber-kildekoden er vert på GitHub. Denne guiden vil vise deg
Bruker du et annet system? Vanilla forum er en åpen kildekode-forumapplikasjon skrevet i PHP. Det er en fullt tilpassbar, enkel å bruke og støtter ekstern
Bruker du et annet system? Mattermost er et åpen kildekode, selvdrevet alternativ til Slack SAAS-meldingstjenesten. Med andre ord, med Mattermost kan du ca
Hva du trenger En Vultr VPS med minst 1 GB RAM. SSH-tilgang (med root/administratorrettigheter). Trinn 1: Installere BungeeCord Først
Plesk-kontrollpanelet har en veldig fin integrasjon for Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt er en av de eneste SSL-leverandørene som gir ut sertifikater komplett
Lets Encrypt er en sertifiseringsinstans dedikert til å tilby SSL-sertifikater gratis. cPanel har bygget en ryddig integrasjon slik at du og din klient
Bruker du et annet system? Concrete5 er et åpen kildekode CMS som tilbyr mange karakteristiske og nyttige funksjoner for å hjelpe redaktører med å produsere innhold enkelt og
Bruker du et annet system? Review Board er et gratis og åpen kildekodeverktøy for gjennomgang av kildekode, dokumentasjon, bilder og mye mer. Det er nettbasert programvare
I denne veiledningen lærer du hvordan du setter opp HTTP-autentisering for en Nginx-webserver som kjører på CentOS 7. Krav For å komme i gang trenger du
Bruker du et annet system? GoAccess er en åpen kildekode-nettlogganalysator. Du kan bruke den til analyse av logger på sanntidsbasis i enten terminalen eller
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) er en åpen kildekode-applikasjon for URL-forkorting og dataanalyse. I denne artikkelen vil vi dekke installasjonsprosessen
Bruker du et annet system? Introduksjon ArangoDB er en åpen kildekode NoSQL-database med en fleksibel datamodell for dokumenter, grafer og nøkkelverdier. Det er
Innledning /etc/-katalogen spiller en kritisk rolle i måten et Linux-system fungerer på. Grunnen til dette er fordi nesten alle systemkonfigurasjoner
Mange systemadministratorer administrerer store mengder servere. Når filer må åpnes på tvers av forskjellige servere, logger du på hver enkelt individuelt ca
Kunstig intelligens er ikke i fremtiden, det er her akkurat i nåtiden I denne bloggen Les hvordan kunstig intelligens-applikasjoner har påvirket ulike sektorer.
Er du også et offer for DDOS-angrep og forvirret over forebyggingsmetodene? Les denne artikkelen for å løse spørsmålene dine.
Du har kanskje hørt at hackere tjener mye penger, men har du noen gang lurt på hvordan tjener de den slags penger? la oss diskutere.
Vil du se revolusjonerende oppfinnelser fra Google og hvordan disse oppfinnelsene forandret livet til alle mennesker i dag? Les deretter til bloggen for å se oppfinnelser fra Google.
Konseptet med selvkjørende biler som skal ut på veiene ved hjelp av kunstig intelligens er en drøm vi har hatt en stund nå. Men til tross for flere løfter, er de ingen steder å se. Les denne bloggen for å lære mer...
Ettersom vitenskapen utvikler seg raskt og tar over mye av innsatsen vår, øker også risikoen for å utsette oss for en uforklarlig singularitet. Les hva singularitet kan bety for oss.
Lagringsmetodene for dataene har vært i utvikling kan være siden fødselen av dataene. Denne bloggen dekker utviklingen av datalagring på grunnlag av en infografikk.
Les bloggen for å kjenne ulike lag i Big Data Architecture og deres funksjoner på den enkleste måten.
I denne digitaldrevne verden har smarthusenheter blitt en avgjørende del av livet. Her er noen fantastiske fordeler med smarthusenheter om hvordan de gjør livet vårt verdt å leve og enklere.
Nylig lanserte Apple macOS Catalina 10.15.4 en tilleggsoppdatering for å fikse problemer, men det ser ut til at oppdateringen forårsaker flere problemer som fører til muring av mac-maskiner. Les denne artikkelen for å lære mer