Asenna Plesk CentOS 7:ään
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Plesk on patentoitu verkkoisäntäohjauspaneeli, jonka avulla käyttäjät voivat hallita henkilökohtaisia ja/tai asiakkaidensa verkkosivustoja, tietokantoja
LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) on yksi Linuxille saatavilla olevista erilaisista levyn salausmuodoista, joka on alustaagnostikko. Tämä opetusohjelma tarjoaa pää- ja sivutusosiot LVM (Linux Volume Manager) -taltion sisällä, joka on salatun LUKS-osion sisällä. Tämän opetusohjelman avulla voit myös avata LUKS-osion lukituksen etänä käyttämällä yksinkertaistettua SSH-palvelindaemonia millä tahansa yhteensopivalla SSH-asiakasohjelmalla.
Valitse Deploy Palvelimet sivun , toimi seuraavasti:
Server Locationosiosta palvelimesi sijainti .CentOS7alla ISO Libraryvälilehdessä Server Typeosiossa.Server Sizeosiosta tarvitsemasi laitteistotiedot .Deploy Nowpainiketta.Käytä View Consolevaihtoehtoa päästäksesi VPS-instanssiin noVNC-konsolin kautta.
Valitse Install CentOS Linux 7vaihtoehto.
Paina Tabnäppäintä.
Syötä textjälkeen, vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quietjotta se näyttää tältä, vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet textja paina Enternäppäintä.
VPS käynnistyy nyt tekstitilan CentOS-asennusohjelmaan. Näet noVNC-konsolissa näytön, kuten alla olevassa kuvassa.

Käytä Alt + Right Arrow Keyyhdistelmää navigoidaksesi TTY2-konsoliin kirjoittaaksesi komentoja komentoriville.
Kirjoita alla olevat komennot luodaksesi osion, joka sisältää GRUB2-käynnistyslataimen, salaamattoman /bootosion ja ensisijaisen osion, joka sisältää LUKS-osion.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Kirjoita seuraava komento näyttääksesi osion asettelun.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Täytä seuraavaksi nimetty rootfsosio näennäissatunnaisilla tiedoilla. Tämä kestää hieman yli puoli tuntia.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
CentOS 7:ssä cryptsetupkomennot käyttävät oletusarvoista salausta aes-xts-plain64, oletusavaimen kokoa 256 bittiä ja oletushajautusarvoa SHA1. Sen sijaan LUKS-osio luodaan turvallisemmalla Serpent-salauksella, jonka avaimen koko on 512 bittiä ja Whirlpool-tiivisteellä.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Syötä vastaukset, kun niitä pyydetään seuraavilla kyselyillä, ja paina sitten Enter-näppäintä:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordVaroitus Tämä sallii pääkäyttäjän kirjautumisen ja kopioinnin ilman salasanakehotetta. Tapa tämä SSH-palvelin, kun olet hakenut /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgtiedoston.
Säilytä kopio LUKS-osion otsikosta. Tämä varmistaa, että jos LUKS-osiosi otsikko on jotenkin vaurioitunut, se voidaan palauttaa. Jos otsikko vaurioituu ilman toimivaa varmuuskopiota, tietosi menetetään lopullisesti.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
Jos haluat kopioida /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgtiedoston palvelimelta, SSH-palvelin on käynnistettävä tilapäisesti käyttämällä suojattua kopiota, joka on suoritettava scpasiakaskoneella sen hakemiseksi.
Kirjoita alla oleva komento luodaksesi SSH-isäntäavaimet.
sshd-keygen
Kirjoita alla oleva komento luodaksesi /etc/ssh/sshd_configtiedoston.
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Kirjoita alla oleva komento muokataksesi /etc/ssh/sshd_configtiedostoa.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Muokkaa tiedostoa painamalla Insert-näppäintä ja siirtyäksesi nuolinäppäimillä tiedoston muokattaviin osiin.
Muuta rivillä yksi numero Port 22oletusarvosta 22valitsemasi satunnaisluvuksi välillä 1025ja 65535. (Esimerkki: portti 25782)
Vieritä alas riville numero kolmetoista, paina End-näppäintä ja paina Enter-näppäintä.
Lisää seuraavalla rivillä HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_keyja paina Enter-näppäintä.
Lisää seuraavalla rivillä HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keyja paina Enter-näppäintä.
Paina Esc-näppäintä, kirjoita :wqja Entertallenna tiedosto painamalla -näppäintä.
Oletusverkkoliitäntä eth0tarvitsee IP-osoitteen. Kirjoita alla oleva komento määrittääksesi esiintymällesi lueteltu IP-osoite eth0verkkoliittymälle.
dhclient
Kirjoita seuraava komento näyttääksesi määritetty IP-osoite. IP-osoite luetellaan välittömästi sen jälkeen inetja ennen netmask. (Esimerkki: inet- 192.0.2.1verkkopeite)
ifconfig eth0
Kirjoita seuraava komento käynnistääksesi SSH-palvelimen.
/usr/sbin/sshd
Jos käytät scpkomentoa asiakaskoneen komentoriviltä, käytä seuraavaa alla olevaa komentoa mallina /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgtiedoston noutamiseen . Korvaa 25782todellisella portin numerolla, joka on määritetty kohdassa /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Korvaa 192.0.2.1todellisella määritetyllä IP-osoitteella.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
luks-header-backup.imgTapa SSH-palvelin heti tiedoston haun jälkeen kirjoittamalla alla oleva komento noVNC-konsoliikkunaan.
killall sshd
Avaa LUKS-osio asettaaksesi LVM:n fyysisen aseman, joka sijaitsee sisällä.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Input the passphrase created earlier to open the LUKS partition when prompted, then press the Enter key.
Enter passphrase for /dev/vda3: strong-password
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named centos, control, live-base and live-rw. The centos is the LUKS partition.
Type the following command below to create the LVM physical volume.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Type the following command below to create the LVM volume group.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for a swap partition. Use sound judgment to create a swap partition, of the necessary size (-L = size of the volume), based on your VPS instance.
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "swap" created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for the root partition. This will use the remaining free space while reserving five percent (5%) to contain LVM snapshots of your logical volumes if you so choose.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "root" created
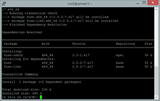
Display the LVM physical volume.
pvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM volume group.
vgdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM logical volume(s).
lvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Type the following command below to deactivate the LVM volume group. This must be completed in order to allow cryptsetup to close the LUKS partition in the next step.
vgchange -a n
When successful, you will receive the following message:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Close the LUKS volume.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
Asiakkaasi järjestelmissä, kohdat 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelyja 3.4. Unlocking using thelukituksen commandon Dracut-Crypt-SSH GitHub sivun joko voimassa tunnuslause nopeaa tai käyttää unlockkomentoa avata LUKS osio irti SSH.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Plesk on patentoitu verkkoisäntäohjauspaneeli, jonka avulla käyttäjät voivat hallita henkilökohtaisia ja/tai asiakkaidensa verkkosivustoja, tietokantoja
Squid on suosittu, ilmainen Linux-ohjelma, jonka avulla voit luoda edelleenlähetysverkkovälityspalvelimen. Tässä oppaassa näet, kuinka Squid asennetaan CentOS:ään kääntääksesi sinut
Johdanto Lighttpd on Apachen haarukka, jonka tarkoituksena on olla paljon vähemmän resurssiintensiivinen. Se on kevyt, tästä syystä sen nimi, ja on melko yksinkertainen käyttää. Asenna
VULTR on äskettäin tehnyt muutoksia heidän omiinsa, ja kaiken pitäisi nyt toimia hyvin heti, kun NetworkManager on käytössä. Jos haluat poistaa käytöstä
Icinga2 on tehokas valvontajärjestelmä, ja master-client-mallissa käytettynä se voi korvata NRPE-pohjaisten valvontatarkastusten tarpeen. Pääasiakas
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Apache Cassandra on ilmainen ja avoimen lähdekoodin NoSQL-tietokannan hallintajärjestelmä, joka on suunniteltu tarjoamaan skaalautuvuutta, hig.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Microweber on avoimen lähdekoodin vedä ja pudota sisällönhallintajärjestelmä ja verkkokauppa. Microweber-lähdekoodia isännöidään GitHubissa. Tämä opas näyttää sinulle
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Mattermost on avoimen lähdekoodin itseisännöity vaihtoehto Slack SAAS -viestipalvelulle. Toisin sanoen Mattermostin avulla voit noin
Mitä tarvitset Vultr VPS:n, jossa on vähintään 1 Gt RAM-muistia. SSH-käyttö (pääkäyttäjän/järjestelmänvalvojan oikeuksilla). Vaihe 1: BungeeCordin asentaminen Ensimmäiset asiat ensin
Plesk-ohjauspaneelissa on erittäin mukava integraatio Lets Encryptille. Lets Encrypt on yksi ainoista SSL-palveluntarjoajista, jotka myöntävät varmenteita täydellisesti
Lets Encrypt on varmenneviranomainen, joka on omistautunut tarjoamaan SSL-varmenteita ilmaiseksi. cPanel on rakentanut siistin integraation sinulle ja asiakkaallesi
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Concrete5 on avoimen lähdekoodin sisällönhallintajärjestelmä, joka tarjoaa monia ainutlaatuisia ja hyödyllisiä ominaisuuksia, jotka auttavat toimittajia tuottamaan sisältöä helposti ja helposti.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Review Board on ilmainen ja avoimen lähdekoodin työkalu lähdekoodin, dokumentaation, kuvien ja monien muiden tarkistamiseen. Se on web-pohjainen ohjelmisto
Tässä oppaassa opit määrittämään HTTP-todennuksen Nginx-verkkopalvelimelle, joka toimii CentOS 7:ssä. Vaatimukset Aloitaksesi tarvitset
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) on avoimen lähdekoodin URL-osoitteiden lyhennys- ja data-analytiikkasovellus. Tässä artikkelissa käsittelemme asennusprosessia
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Johdanto ArangoDB on avoimen lähdekoodin NoSQL-tietokanta, jossa on joustava tietomalli asiakirjoille, kaavioille ja avainarvoille. se on
Johdanto /etc/-hakemistolla on tärkeä rooli Linux-järjestelmän toiminnassa. Syynä tähän on se, että lähes kaikki järjestelmäkokoonpanot
Monet järjestelmänvalvojat hallitsevat suuria määriä palvelimia. Kun tiedostoja on käytettävä eri palvelimien kautta, kirjaudu jokaiseen erikseen n
Tämä opetusohjelma kattaa Half Life 2 -pelipalvelimen asennuksen CentOS 6 -järjestelmään. Vaihe 1: Edellytysten asentaminen Voit määrittää ou
Laravel GitScrum tai GitScrum on avoimen lähdekoodin tuottavuustyökalu, joka on suunniteltu auttamaan kehitysryhmiä ottamaan käyttöön Scrum-metodologian samalla tavalla.
Tekoäly ei ole tulevaisuudessa, se tässä nykyisyydessä Tässä blogissa Lue kuinka tekoälysovellukset ovat vaikuttaneet eri sektoreihin.
Oletko myös DDOS-hyökkäysten uhri ja hämmentynyt ehkäisymenetelmistä? Lue tämä artikkeli ratkaistaksesi kysymyksesi.
Olet ehkä kuullut, että hakkerit ansaitsevat paljon rahaa, mutta oletko koskaan miettinyt, kuinka he ansaitsevat tuollaista rahaa? keskustellaan.
Haluatko nähdä Googlen vallankumouksellisia keksintöjä ja kuinka nämä keksinnöt muuttivat jokaisen ihmisen elämää nykyään? Lue sitten blogia nähdäksesi Googlen keksinnöt.
Konsepti itseohjautuvista autoista lähteä tielle tekoälyn avulla on ollut haaveena jo jonkin aikaa. Mutta useista lupauksista huolimatta niitä ei näy missään. Lue tämä blogi saadaksesi lisätietoja…
Kun tiede kehittyy nopeasti ja ottaa haltuunsa suuren osan ponnisteluistamme, myös riskit altistaa itsemme selittämättömälle singulariteetille kasvavat. Lue, mitä singulaarisuus voisi tarkoittaa meille.
Tietojen säilytystavat ovat kehittyneet mahdollisesti Datan syntymästä lähtien. Tämä blogi käsittelee tiedon tallennuksen kehitystä infografian pohjalta.
Blogista saat tietää Big Data -arkkitehtuurin eri kerroksista ja niiden toiminnoista yksinkertaisimmalla tavalla.
Tässä digitaalisessa maailmassa kodin älylaitteista on tullut tärkeä osa elämää. Tässä on muutamia älykkäiden kodin laitteiden hämmästyttäviä etuja, joiden avulla ne tekevät elämästämme elämisen arvoista ja yksinkertaisempaa.
Apple julkaisi äskettäin macOS Catalina 10.15.4 -lisäpäivityksen ongelmien korjaamiseksi, mutta näyttää siltä, että päivitys aiheuttaa lisää ongelmia, jotka johtavat mac-koneiden tiilikaamiseen. Lue tämä artikkeli saadaksesi lisätietoja