Asenna Plesk CentOS 7:ään
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Plesk on patentoitu verkkoisäntäohjauspaneeli, jonka avulla käyttäjät voivat hallita henkilökohtaisia ja/tai asiakkaidensa verkkosivustoja, tietokantoja
H2O on uuden sukupolven HTTP-palvelin, jossa on erinomaiset, täysin varustetut HTTP/2-toteutukset kaikista nykyisistä käytössä olevista web-palvelimista. Kun H2O on verkkopalvelimesi, voit hyödyntää HTTP/2-määrityksen uusia ominaisuuksia, kuten latenssioptimointia, palvelinpush- ja palvelinpuolen priorisointia, jotka voivat hyödyntää nykyaikaisia selaimen ominaisuuksia, joista harvoin puhutaan.
Tässä yksityiskohtaisessa opetusohjelmassa näytän sinulle vaihe vaiheelta, kuinka H2O saadaan toimimaan CentOS 7 x64 -esiintymässäsi.
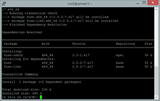
Kirjaudu sisään SSH:n kautta ilmentymäsi alla olevilla tunnistetiedoilla ja päivitä järjestelmä seuraavasti.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
Jotta voit asentaa H2O:n CentOS 7:ään, sinun on lisättävä Bintray RPM -tietovarasto esirakennettujen H2O-binäärien asentamiseksi. Käytä Nano-editoria luodaksesi mukautetun repon.
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-h2o-rpm.repo
Kopioi ja liitä alla oleva teksti repo-tiedostoon.
[bintray-h2o-rpm]
name=bintray-h2o-rpm
baseurl=https://dl.bintray.com/tatsushid/h2o-rpm/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Asenna seuraavaksi H2O.
sudo yum install h2o -y
Nyt kun H2O on asennettu, mutta ennen kuin otat palvelun käyttöön ja käynnistät sen, oikea konfigurointi vaaditaan ja meidän on luotava erityinen käyttäjä ja ryhmä H2O:ta varten. Luo ryhmä ja käyttäjä H2O:ta varten nimellä h2o.
sudo groupadd -g 101 h2o
sudo useradd -d /etc/h2o -g 101 -M -s /sbin/nologin -u 101 h2o
Seuraavat vaiheet antavat esimerkkejä määritysasetuksista eri unencrypted, encrypted, staticja dynamicpalvelinasennuksille; sekä kaikkien neljän yhdistelmä.
http://www.example.comTo http://example.com(staattisia HTML-sivuja, ei PHP) KokoonpanoSiirry /etc/h2o/hakemistoon.
cd /etc/h2o/
Nimeä oletuksena h2o.confon h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Luo uusi h2o.conftiedosto.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopioi ja liitä alla oleva teksti h2o.conftiedostoon.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Ota käyttöön ja käynnistä H2O-palvelin.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Luo oletusarvo index.htmlkäyttämällä mallia yllä /var/www/htmlolevaan hakemistovaihtoehtoon file.dirkohdassa /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Avaa nyt selaimesi ja kirjoita esiintymäsi palvelimen verkkotunnus ( example.comtai www.example.com). Saatko viestin Unable to connecttai This site can’t be reachedviestin? CentOS:n oletuspalomuuriasetus estää saapuvat yhteydet http-porttiin. Avaa se suorittamalla seuraava.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Päivitä sivu selaimessasi ( F5), niin saat tämän viestin.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.comTo http://www.example.com(staattisia HTML-sivuja, ei PHP) KokoonpanoSiirry /etc/h2o/hakemistoon.
cd /etc/h2o/
Nimeä oletuksena h2o.confon h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Luo uusi h2o.conftiedosto.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopioi ja liitä seuraava teksti h2o.conftiedostoon.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Ota käyttöön ja käynnistä H2O-palvelin.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Luo oletustiedosto index.htmlkäyttämällä mallia yllä /var/www/htmlolevaan hakemistovaihtoehtoon file.dirkohdassa /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Avaa nyt selaimesi ja kirjoita esiintymäsi palvelimen verkkotunnus ( example.comtai www.example.com). Saatko viestin Unable to connecttai This site can’t be reachedviestin? CentOS:n oletuspalomuuriasetus estää saapuvat yhteydet http-porttiin. Avaa se seuraavasti.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Päivitä sivu selaimessasi ( F5), niin saat tämän viestin.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://www.example.comTo http://example.com(dynaamisia, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) KokoonpanoSiirry /etc/h2o/hakemistoon.
cd /etc/h2o/
Nimeä oletuksena h2o.confon h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Luo uusi h2o.conftiedosto.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopioi ja liitä seuraava teksti h2o.conftiedostoon.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://www.example.com To http://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text into the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Suorita bash-komentosarja ensimmäistä kertaa, koska H2O ei käynnisty kunnolla, jos sitä ei luoda. Tämän luominen vie noin minuutin tai kaksi ensimmäisellä kerralla.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
PHP:n käsittelyä varten PHP-FPM 7.1 -daemon on asennettava ja määritettävä. PHP-FPM:n oletusversiota 5.4.x uudemman version asentamiseksi on asennettava REMI-repo, joka sisältää PHP-versiot 5.6.x, 7.0.x ja 7.1.x. Asenna PHP-versio 7.1.x kirjoittamalla seuraavat komennot.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Siirry /etc/opt/remi/php71/hakemistoon.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Nimeä oletuksena php-fpm.confon php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Luo uusi php-fpm.conftiedosto.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Kopioi ja liitä seuraava teksti php-fpm.conftiedostoon.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Nimeä hakemiston oletustiedosto www.confuudelleen php-fpm.d.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Luo uusi www.conftiedosto.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Kopioi ja liitä alla oleva teksti www.conftiedostoon. Muuta pm.max\_childrenvastaamaan suorittimien määrää VPS-instanssisi mukaan.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Nimeä oletustiedosto uudelleen php.ini.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Luo uusi php.initiedosto.
sudo nano php.ini
Kopioi ja liitä alla oleva teksti uuteen php.ini file. Muuta memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesizeja date.timezoneVPS-instanssisi mukaisesti.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Muuta /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/hakemiston ryhmän omistajuus apacheryhmästä h2oryhmäksi.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Luo hakemisto, jossa PHP-FPM-palvelimen lokit sijaitsevat.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Ota käyttöön ja käynnistä PHP-FPM-palvelin.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Ota käyttöön ja käynnistä H2O-palvelin.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Luo hakemisto, jossa oletusarvo index.phpsijaitsee file.diryllä olevan hakemistovaihtoehdon mukaan /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Luo oletus index.phpkäyttäen phpinfokomentoa testata PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Kopioi ja liitä alla oleva teksti uuteen index.phptiedostoon.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Avaa nyt selaimesi ja kirjoita esiintymäsi palvelimen verkkotunnus ( example.comtai www.example.com). Saatko viestin Unable to connecttai This site can’t be reachedviestin? CentOS:n oletuspalomuuriasetus estää saapuvat yhteydet http-porttiin. Avaa se seuraavasti.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Päivitä sivu selaimessasi ( F5), niin saat normaalin PHP-tietosivun.
Tämä päättää opetusohjelmani. Kiitos kun luit.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Plesk on patentoitu verkkoisäntäohjauspaneeli, jonka avulla käyttäjät voivat hallita henkilökohtaisia ja/tai asiakkaidensa verkkosivustoja, tietokantoja
Squid on suosittu, ilmainen Linux-ohjelma, jonka avulla voit luoda edelleenlähetysverkkovälityspalvelimen. Tässä oppaassa näet, kuinka Squid asennetaan CentOS:ään kääntääksesi sinut
Johdanto Lighttpd on Apachen haarukka, jonka tarkoituksena on olla paljon vähemmän resurssiintensiivinen. Se on kevyt, tästä syystä sen nimi, ja on melko yksinkertainen käyttää. Asenna
VULTR on äskettäin tehnyt muutoksia heidän omiinsa, ja kaiken pitäisi nyt toimia hyvin heti, kun NetworkManager on käytössä. Jos haluat poistaa käytöstä
Icinga2 on tehokas valvontajärjestelmä, ja master-client-mallissa käytettynä se voi korvata NRPE-pohjaisten valvontatarkastusten tarpeen. Pääasiakas
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Apache Cassandra on ilmainen ja avoimen lähdekoodin NoSQL-tietokannan hallintajärjestelmä, joka on suunniteltu tarjoamaan skaalautuvuutta, hig.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Microweber on avoimen lähdekoodin vedä ja pudota sisällönhallintajärjestelmä ja verkkokauppa. Microweber-lähdekoodia isännöidään GitHubissa. Tämä opas näyttää sinulle
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Mattermost on avoimen lähdekoodin itseisännöity vaihtoehto Slack SAAS -viestipalvelulle. Toisin sanoen Mattermostin avulla voit noin
Mitä tarvitset Vultr VPS:n, jossa on vähintään 1 Gt RAM-muistia. SSH-käyttö (pääkäyttäjän/järjestelmänvalvojan oikeuksilla). Vaihe 1: BungeeCordin asentaminen Ensimmäiset asiat ensin
Plesk-ohjauspaneelissa on erittäin mukava integraatio Lets Encryptille. Lets Encrypt on yksi ainoista SSL-palveluntarjoajista, jotka myöntävät varmenteita täydellisesti
Lets Encrypt on varmenneviranomainen, joka on omistautunut tarjoamaan SSL-varmenteita ilmaiseksi. cPanel on rakentanut siistin integraation sinulle ja asiakkaallesi
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Concrete5 on avoimen lähdekoodin sisällönhallintajärjestelmä, joka tarjoaa monia ainutlaatuisia ja hyödyllisiä ominaisuuksia, jotka auttavat toimittajia tuottamaan sisältöä helposti ja helposti.
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Review Board on ilmainen ja avoimen lähdekoodin työkalu lähdekoodin, dokumentaation, kuvien ja monien muiden tarkistamiseen. Se on web-pohjainen ohjelmisto
Tässä oppaassa opit määrittämään HTTP-todennuksen Nginx-verkkopalvelimelle, joka toimii CentOS 7:ssä. Vaatimukset Aloitaksesi tarvitset
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) on avoimen lähdekoodin URL-osoitteiden lyhennys- ja data-analytiikkasovellus. Tässä artikkelissa käsittelemme asennusprosessia
Käytätkö erilaista järjestelmää? Johdanto ArangoDB on avoimen lähdekoodin NoSQL-tietokanta, jossa on joustava tietomalli asiakirjoille, kaavioille ja avainarvoille. se on
Johdanto /etc/-hakemistolla on tärkeä rooli Linux-järjestelmän toiminnassa. Syynä tähän on se, että lähes kaikki järjestelmäkokoonpanot
Monet järjestelmänvalvojat hallitsevat suuria määriä palvelimia. Kun tiedostoja on käytettävä eri palvelimien kautta, kirjaudu jokaiseen erikseen n
Tämä opetusohjelma kattaa Half Life 2 -pelipalvelimen asennuksen CentOS 6 -järjestelmään. Vaihe 1: Edellytysten asentaminen Voit määrittää ou
Laravel GitScrum tai GitScrum on avoimen lähdekoodin tuottavuustyökalu, joka on suunniteltu auttamaan kehitysryhmiä ottamaan käyttöön Scrum-metodologian samalla tavalla.
Tekoäly ei ole tulevaisuudessa, se tässä nykyisyydessä Tässä blogissa Lue kuinka tekoälysovellukset ovat vaikuttaneet eri sektoreihin.
Oletko myös DDOS-hyökkäysten uhri ja hämmentynyt ehkäisymenetelmistä? Lue tämä artikkeli ratkaistaksesi kysymyksesi.
Olet ehkä kuullut, että hakkerit ansaitsevat paljon rahaa, mutta oletko koskaan miettinyt, kuinka he ansaitsevat tuollaista rahaa? keskustellaan.
Haluatko nähdä Googlen vallankumouksellisia keksintöjä ja kuinka nämä keksinnöt muuttivat jokaisen ihmisen elämää nykyään? Lue sitten blogia nähdäksesi Googlen keksinnöt.
Konsepti itseohjautuvista autoista lähteä tielle tekoälyn avulla on ollut haaveena jo jonkin aikaa. Mutta useista lupauksista huolimatta niitä ei näy missään. Lue tämä blogi saadaksesi lisätietoja…
Kun tiede kehittyy nopeasti ja ottaa haltuunsa suuren osan ponnisteluistamme, myös riskit altistaa itsemme selittämättömälle singulariteetille kasvavat. Lue, mitä singulaarisuus voisi tarkoittaa meille.
Tietojen säilytystavat ovat kehittyneet mahdollisesti Datan syntymästä lähtien. Tämä blogi käsittelee tiedon tallennuksen kehitystä infografian pohjalta.
Blogista saat tietää Big Data -arkkitehtuurin eri kerroksista ja niiden toiminnoista yksinkertaisimmalla tavalla.
Tässä digitaalisessa maailmassa kodin älylaitteista on tullut tärkeä osa elämää. Tässä on muutamia älykkäiden kodin laitteiden hämmästyttäviä etuja, joiden avulla ne tekevät elämästämme elämisen arvoista ja yksinkertaisempaa.
Apple julkaisi äskettäin macOS Catalina 10.15.4 -lisäpäivityksen ongelmien korjaamiseksi, mutta näyttää siltä, että päivitys aiheuttaa lisää ongelmia, jotka johtavat mac-koneiden tiilikaamiseen. Lue tämä artikkeli saadaksesi lisätietoja