Įdiekite „Plesk“ „CentOS 7“.
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Plesk yra patentuotas žiniatinklio prieglobos valdymo skydelis, leidžiantis vartotojams administruoti savo asmenines ir (arba) klientų svetaines, duomenų bazes
LUKS („Linux Unified Key Setup“) yra vienas iš įvairių „Linux“ galimų disko šifravimo formatų, kuris yra agnostikas. Šioje instrukcijoje rasite pagrindinius ir apsikeitimo skaidinius LVM („Linux Volume Manager“) tome, esančiame užšifruotame LUKS skaidinyje. Ši pamoka taip pat leidžia nuotoliniu būdu atrakinti LUKS skaidinį naudojant supaprastintą SSH serverio demoną, naudojant bet kurią suderinamą SSH kliento programą.
Puslapyje Diegti serverius atlikite šiuos veiksmus:
Server LocationSkyriuje pasirinkite savo serverio vietą .CentOS7po skilties ISO Libraryskirtuku Server Type.Server SizeSkyriuje pasirinkite reikiamas techninės įrangos specifikacijas .Deploy Nowmygtuką.Naudokite View Consoleparinktį, kad pasiektumėte VPS egzempliorių per noVNC konsolę.
Pasirinkite Install CentOS Linux 7parinktį.
Paspauskite Tabklavišą.
Įveskite textpo vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet, kad atrodytų taip, vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet textir paspauskite Enterklavišą.
VPS dabar bus paleistas į teksto režimo CentOS diegimo programą. Pamatysite ekraną noVNC konsolėje, kaip parodyta paveikslėlyje žemiau.

Naudokite šį Alt + Right Arrow Keyderinį, kad pereitumėte į TTY2 pultą ir įvestumėte komandas komandų eilutėje.
Toliau įveskite šias komandas, kad sukurtumėte skaidinį, kuriame būtų GRUB2 įkrovos įkroviklis, nešifruotas /bootskaidinys ir pirminis skaidinys, kuriame bus LUKS skaidinys.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Įveskite šią komandą, kad būtų rodomas skaidinio išdėstymas.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Tada užpildykite pavadintą rootfsskaidinį pseudoatsitiktiniais duomenimis. Tai užtruks šiek tiek daugiau nei pusvalandį.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
„CentOS 7“ cryptsetupkomandose naudojamas numatytasis šifras aes-xts-plain64, numatytasis 256 bitų rakto dydis ir numatytasis SHA1 maišas. Vietoj to, LUKS skaidinys bus sukurtas naudojant saugesnį Serpent šifrą, kurio rakto dydis yra 512 bitų ir su Whirlpool maiša.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Įveskite atsakymus, kai būsite paraginti pateikti šias užklausas, tada paspauskite Enterklavišą:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordĮspėjimas Tai leis root prisijungti ir kopijuoti be slaptažodžio raginimo. Gavus /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfailą, užmuškite šį SSH serverį .
Kad apsaugotumėte, išsaugokite LUKS skaidinio antraštės kopiją. Tai užtikrina, kad jei jūsų LUKS skaidinio antraštė bus kažkaip pažeista, ją bus galima atkurti. Jei antraštė sugadinta be veikiančios atsarginės kopijos, jūsų duomenys prarandami visam laikui.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
Norint nukopijuoti /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfailą iš serverio, SSH serveris turi būti laikinai paleistas, naudojant saugią kopiją, vykdomą scpkliento priegloboje, kad jį nuskaitytų.
Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad sugeneruotumėte SSH pagrindinio kompiuterio raktus.
sshd-keygen
Norėdami sukurti /etc/ssh/sshd_configfailą, įveskite toliau pateiktą komandą .
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Norėdami redaguoti /etc/ssh/sshd_configfailą, įveskite toliau pateiktą komandą .
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Norėdami redaguoti failą, paspauskite Insertklavišą ir naudokite rodyklių klavišus, kad pereitumėte į failo dalis, kurias reikia redaguoti.
Pirmoje eilutėje pakeiskite skaičių Port 22iš numatytojo 22į atsitiktinį pasirinktą skaičių tarp 1025ir 65535. (Pavyzdys: prievadas 25782)
Slinkite žemyn iki tryliktos eilutės, paspauskite Endklavišą ir paspauskite Enterklavišą.
Kitoje eilutėje pridėkite HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_keyir paspauskite Enterklavišą.
Kitoje eilutėje pridėkite HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keyir paspauskite Enterklavišą.
Paspauskite Escklavišą, įveskite :wqir paspauskite Enterklavišą, kad išsaugotumėte failą.
Numatytajai tinklo sąsajai eth0reikalingas IP adresas. Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad eth0tinklo sąsajai priskirtumėte savo egzemplioriaus IP adresą .
dhclient
Įveskite šią komandą, kad būtų rodomas priskirtas IP adresas. IP adresas bus pateiktas iškart po inetir prieš netmask. (Pavyzdys: inet 192.0.2.1tinklo kaukė)
ifconfig eth0
Įveskite šią komandą, kad paleistumėte SSH serverį.
/usr/sbin/sshd
Jei naudojate scpkomandą iš komandinės eilutės kliento kompiuteryje, naudokite toliau pateiktą komandą kaip šabloną, kad gautumėte /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfailą. Pakeiskite 25782tikruoju prievado numeriu, priskirtu /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Pakeiskite 192.0.2.1tikruoju priskirtu IP adresu.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
Gavus luks-header-backup.imgfailą, nedelsdami užmuškite SSH serverį įvesdami žemiau esančią komandą noVNC konsolės lange.
killall sshd
Atidarykite LUKS skaidinį, kad nustatytumėte LVM fizinį tomą, kuris bus viduje.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Įveskite anksčiau sukurtą slaptafrazę, kad atidarytumėte LUKS skaidinį, kai būsite paraginti, tada paspauskite Enterklavišą.
Įveskite slaptafrazę /dev/vda3:strong-password
Toliau įveskite šią komandą:
ls /dev/mapper
Jame bus pateikta šiuos failus pavadintas centos, control, live-baseir live-rw. Tai centosyra LUKS skaidinys.
Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad sukurtumėte LVM fizinį tomą.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
Kai pasiseks, gausite tokį pranešimą:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad sukurtumėte LVM tomo grupę.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
Kai pasiseks, gausite tokį pranešimą:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad sukurtumėte LVM loginį tomą apsikeitimo skaidiniui. Remdamiesi savo VPS egzemplioriumi, sukurkite reikiamo dydžio apsikeitimo skaidinį (-L = tūrio dydis).
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
Kai pasiseks, gausite tokį pranešimą:
Logical volume "swap" created
Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad sukurtumėte LVM loginį tomą šakniniam skaidiniui. Tai išnaudos likusią laisvą vietą ir rezervuos penkis procentus (5 %) LVM momentinėms loginių tomų nuotraukoms, jei pasirinksite.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
Kai pasiseks, gausite tokį pranešimą:
Logical volume "root" created
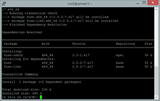
Rodyti LVM fizinį tūrį.
pvdisplay
Pamatysite tekstą noVNC konsolėje, panašų į tai, kas pavaizduota toliau esančiame paveikslėlyje.

Rodyti LVM garsumo grupę.
vgdisplay
Pamatysite tekstą noVNC konsolėje, panašų į tai, kas pavaizduota toliau esančiame paveikslėlyje.

Rodyti LVM loginį tomą (-us).
lvdisplay
Pamatysite tekstą noVNC konsolėje, panašų į tai, kas pavaizduota toliau esančiame paveikslėlyje.

Toliau įveskite šią komandą, kad išjungtumėte LVM tomo grupę. Tai turi būti atlikta, kad cryptsetupkitame veiksme būtų galima uždaryti LUKS skaidinį.
vgchange -a n
Kai pasiseks, gausite tokį pranešimą:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Uždarykite LUKS tomą.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Toliau įveskite šią komandą:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
Savo klientų sistemų, skaitykite skyriuose 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelyir 3.4. Unlocking using theatrakinti commandiš Dracut-Kripta-SSH GitHub puslapyje , kad abiejų galioti slaptažodis laiku arba naudoti unlockkomandą atidaryti savo LUKS pertvara iš savo SSH klientas.
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Plesk yra patentuotas žiniatinklio prieglobos valdymo skydelis, leidžiantis vartotojams administruoti savo asmenines ir (arba) klientų svetaines, duomenų bazes
Squid yra populiari nemokama „Linux“ programa, leidžianti sukurti persiuntimo žiniatinklio tarpinį serverį. Šiame vadove pamatysite, kaip įdiegti „Squid“ „CentOS“, kad paverstumėte jus
Įvadas Lighttpd yra „Apache“ šakutė, skirta daug mažiau išteklių imti. Jis yra lengvas, todėl jo pavadinimas ir yra gana paprastas naudoti. Įdiegti
VULTR neseniai atliko pakeitimus, ir dabar viskas turėtų veikti gerai, kai įjungta „NetworkManager“. Jei norite išjungti
Icinga2 yra galinga stebėjimo sistema, o kai naudojama pagrindinio kliento modelyje, ji gali pakeisti NRPE pagrįstų stebėjimo patikrų poreikį. Meistras-klientas
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Apache Cassandra yra nemokama ir atviro kodo NoSQL duomenų bazių valdymo sistema, skirta užtikrinti mastelio keitimą, hig.
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Mattermost yra atvirojo kodo, savarankiškai priglobta alternatyva Slack SAAS pranešimų paslaugai. Kitaip tariant, naudodami Mattermost, jūs apytiksliai
„Plesk“ valdymo skydelyje yra labai graži „Lets Encrypt“ integracija. „Lets Encrypt“ yra vienas iš vienintelių SSL teikėjų, išduodančių visus sertifikatus
„Lets Encrypt“ yra sertifikatų institucija, skirta nemokamai teikti SSL sertifikatus. cPanel sukūrė tvarkingą integraciją, kad jūs ir jūsų klientas
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Concrete5 yra atvirojo kodo TVS, kuri siūlo daug išskirtinių ir naudingų funkcijų, padedančių redaktoriams lengvai sukurti turinį
Naudojate kitą sistemą? „Review Board“ yra nemokamas atvirojo kodo įrankis, skirtas šaltinio kodui, dokumentacijai, vaizdams ir daugeliui kitų peržiūrėti. Tai internetinė programinė įranga
Šiame vadove sužinosite, kaip nustatyti HTTP autentifikavimą Nginx žiniatinklio serveriui, kuriame veikia CentOS 7. Reikalavimai Norėdami pradėti, jums reikės
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) yra atvirojo kodo URL sutrumpinimo ir duomenų analizės programa. Šiame straipsnyje apžvelgsime diegimo procesą
Naudojate kitą sistemą? Įvadas ArangoDB yra atvirojo kodo NoSQL duomenų bazė su lanksčiu duomenų modeliu dokumentams, grafikams ir raktų reikšmėms. tai yra
Įvadas Katalogas /etc/ vaidina lemiamą vaidmenį veikiant Linux sistemai. Taip yra todėl, kad beveik visos sistemos konfigūracijos
Daugelis sistemos administratorių valdo didelius serverių kiekius. Kai failus reikia pasiekti skirtinguose serveriuose, prisijungiant prie kiekvieno atskirai apytiksliai
Ši pamoka apims Half Life 2 žaidimų serverio diegimą CentOS 6 sistemoje. 1 veiksmas: būtinų sąlygų įdiegimas Norėdami nustatyti ou
Laravel GitScrum arba GitScrum yra atvirojo kodo produktyvumo įrankis, skirtas padėti kūrimo komandoms įgyvendinti Scrum metodiką panašiai
Įvadas Šiame „Vultr“ vadove sužinosite, kaip įdiegti „PowerDNS“. PowerDNS yra programa, skirta paleisti savo vardų serverius. Tai labai naudinga, kai
Galite nukopijuoti ir įklijuoti šį bash scenarijų į Vultr valdymo skydelio paleisties scenarijaus sritį. Jis įdiegs visus reikalingus paketus į ru
Dirbtinis intelektas nėra ateityje, jis čia, dabartyje Šiame tinklaraštyje Skaitykite, kaip dirbtinio intelekto programos paveikė įvairius sektorius.
Ar taip pat esate DDOS atakų auka ir esate sumišęs dėl prevencijos metodų? Perskaitykite šį straipsnį, kad išspręstumėte savo užklausas.
Galbūt girdėjote, kad įsilaužėliai uždirba daug pinigų, bet ar kada susimąstėte, kaip jie uždirba tokius pinigus? padiskutuokime.
Ar norite pamatyti revoliucinius „Google“ išradimus ir kaip šie išradimai pakeitė kiekvieno žmogaus gyvenimą šiandien? Tada skaitykite tinklaraštį, kad pamatytumėte „Google“ išradimus.
Savavaledžių automobilių koncepcija, kuri išvažiuotų į kelius su dirbtinio intelekto pagalba, yra svajonė, kurią jau kurį laiką svajojame. Tačiau nepaisant kelių pažadų, jų niekur nematyti. Skaitykite šį tinklaraštį, kad sužinotumėte daugiau…
Kadangi mokslas sparčiai vystosi, perimdamas daug mūsų pastangų, taip pat didėja rizika, kad pateksime į nepaaiškinamą singuliarumą. Skaitykite, ką mums gali reikšti išskirtinumas.
Duomenų saugojimo metodai gali būti tobulinami nuo pat Duomenų gimimo. Šiame tinklaraštyje, remiantis infografika, aprašoma duomenų saugojimo raida.
Skaitykite tinklaraštį, kad paprasčiausiai sužinotumėte apie skirtingus didžiųjų duomenų architektūros sluoksnius ir jų funkcijas.
Šiame skaitmeniniu būdu pagrįstame pasaulyje išmanieji namų įrenginiai tapo svarbia gyvenimo dalimi. Štai keletas nuostabių išmaniųjų namų įrenginių privalumų, kaip jie daro mūsų gyvenimą vertą gyventi ir paprastesnį.
Neseniai „Apple“ išleido „macOS Catalina 10.15.4“ priedą, skirtą problemoms išspręsti, tačiau atrodo, kad dėl atnaujinimo kyla daugiau problemų, dėl kurių „Mac“ įrenginiai blokuojami. Norėdami sužinoti daugiau, perskaitykite šį straipsnį