Telepítse a Plesket a CentOS 7 rendszeren
Más rendszert használ? A Plesk egy szabadalmaztatott webtárhely-vezérlőpult, amely lehetővé teszi a felhasználók számára, hogy adminisztrálják személyes és/vagy ügyfeleik webhelyeit, adatbázisait
A LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) a Linux számára elérhető különféle lemeztitkosítási formátumok egyike, amely platform agnosztikus. Ez az oktatóanyag gyökér és swap partíciókat biztosít egy LVM (Linux Volume Manager) köteten belül, amely egy titkosított LUKS partíción belül található. Ez az oktatóanyag lehetővé teszi a LUKS-partíció távoli feloldását is egy egyszerűsített SSH-kiszolgáló démon segítségével, bármilyen kompatibilis SSH-kliensprogram használatával.
A Kiszolgálók telepítése oldalon tegye a következőket:
Server Locationrészben.CentOS7alatt ISO Librarylapján Server Typerészben.Server Sizerészben.Deploy Nowgombra.Használja a View Consolelehetőséget a VPS-példány eléréséhez a noVNC konzolon keresztül.
Válassza ki a Install CentOS Linux 7lehetőséget.
Nyomja meg a Tabgombot.
Írja be az textután vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet, hogy így nézzen ki, vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet textés nyomja meg a Entergombot.
A VPS most a szöveges módú CentOS telepítőbe fog indulni. Látni fog egy képernyőt a noVNC konzolon, mint az alábbi képen.

A Alt + Right Arrow Keykombináció segítségével navigáljon a TTY2 konzolra, és írja be a parancsokat a parancssorba.
Írja be az alábbi parancsokat egy partíció létrehozásához, amely tartalmazza a GRUB2 rendszertöltőt, egy titkosítatlan /bootpartíciót és egy elsődleges partíciót, amely a LUKS partíciót fogja tárolni.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Írja be a következő parancsot a partíció elrendezésének megjelenítéséhez.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Ezután töltse fel a megnevezett rootfspartíciót pszeudo-véletlen adatokkal. Ez valamivel több mint fél órát vesz igénybe.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
A CentOS 7 rendszeren a cryptsetupparancsok az alapértelmezett titkosítást aes-xts-plain64, az alapértelmezett 256 bites kulcsméretet és az SHA1 alapértelmezett kivonatát használják. Ehelyett a LUKS partíció a biztonságosabb Serpent titkosítással, 512 bites kulcsmérettel és a Whirlpool hash-el jön létre.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Írja be a válaszokat, amikor a következő lekérdezéseket kéri, majd nyomja meg a Entergombot:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordFigyelmeztetés Ez lehetővé teszi a root bejelentkezést és a jelszókérés nélküli másolást. A /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfájl lekérése után állítsa le ezt az SSH-kiszolgálót .
A biztonság kedvéért mentse el a LUKS partíció fejlécének másolatát. Ez biztosítja, hogy ha a LUKS partíció fejléce valamilyen módon megsérül, az visszaállítható. Ha a fejléc működő biztonsági mentés nélkül megsérül, az adatok örökre elvesznek.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
A /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfájl kiszolgálóról történő másolásához ideiglenesen el kell indítani egy SSH-kiszolgálót, az ügyfélgazdagépen végrehajtható biztonságos másolatot használva a scpletöltéshez.
Írja be az alábbi parancsot az SSH-gazdakulcsok generálásához.
sshd-keygen
Írja be az alábbi parancsot a /etc/ssh/sshd_configfájl létrehozásához .
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Írja be az alábbi parancsot a /etc/ssh/sshd_configfájl szerkesztéséhez .
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
A fájl szerkesztéséhez nyomja meg a Insertgombot, és a nyílbillentyűkkel navigáljon a fájl szerkesztendő részeihez.
Az első sorban módosítsa a számot Port 22az alapértelmezett 22értékről egy véletlenszerű számra a 1025és között 65535. (Példa: port 25782)
Görgessen le a tizenharmadik sorig, nyomja meg a Endgombot, majd nyomja meg a Entergombot.
A következő sorban adja hozzá, HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_keyés nyomja meg a Entergombot.
A következő sorban adja hozzá, HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keyés nyomja meg a Entergombot.
Nyomja meg a Escgombot, írja be, :wqés nyomja meg a Entergombot a fájl mentéséhez.
Az alapértelmezett hálózati interfésznek eth0szüksége van egy IP-címre. Írja be az alábbi parancsot, hogy a példányához tartozó IP-címet hozzárendelje a eth0hálózati interfészhez.
dhclient
Írja be a következő parancsot a hozzárendelt IP-cím megjelenítéséhez. Az IP-cím közvetlenül utána inetés előtt jelenik meg netmask. (Példa: inet 192.0.2.1hálózati maszk)
ifconfig eth0
Írja be a következő parancsot az SSH-kiszolgáló elindításához.
/usr/sbin/sshd
Ha a scpparancsot parancssorból használja egy ügyfélgépen, használja az alábbi parancsot sablonként a /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgfájl lekéréséhez . Cserélje 25782ki a tényleges portszámot, amely a /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Cserélje 192.0.2.1ki a ténylegesen hozzárendelt IP-címet.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
A luks-header-backup.imgfájl visszakeresése után azonnal ölje meg az SSH-kiszolgálót az alábbi parancs beírásával a noVNC konzolablakba.
killall sshd
Nyissa meg a LUKS partíciót a benne található LVM fizikai kötet beállításához.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Input the passphrase created earlier to open the LUKS partition when prompted, then press the Enter key.
Enter passphrase for /dev/vda3: strong-password
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named centos, control, live-base and live-rw. The centos is the LUKS partition.
Type the following command below to create the LVM physical volume.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Type the following command below to create the LVM volume group.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for a swap partition. Use sound judgment to create a swap partition, of the necessary size (-L = size of the volume), based on your VPS instance.
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "swap" created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for the root partition. This will use the remaining free space while reserving five percent (5%) to contain LVM snapshots of your logical volumes if you so choose.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "root" created
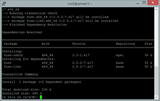
Display the LVM physical volume.
pvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM volume group.
vgdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM logical volume(s).
lvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Type the following command below to deactivate the LVM volume group. This must be completed in order to allow cryptsetup to close the LUKS partition in the next step.
vgchange -a n
When successful, you will receive the following message:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Close the LUKS volume.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
Kliensrendszerein tekintse meg a Dracut-Crypt-SSH GitHub oldal szakaszait 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelyés 3.4. Unlocking using theoldja commandfel a zárolást , hogy kényszerítse a jelszót, vagy használja a parancsot a LUKS-partíció megnyitásához az SSH-ügyfélről.unlock
Más rendszert használ? A Plesk egy szabadalmaztatott webtárhely-vezérlőpult, amely lehetővé teszi a felhasználók számára, hogy adminisztrálják személyes és/vagy ügyfeleik webhelyeit, adatbázisait
A Squid egy népszerű, ingyenes Linux-program, amely lehetővé teszi továbbítási webproxy létrehozását. Ebben az útmutatóban megtudhatja, hogyan telepítheti a Squid-et a CentOS rendszerre, hogy megfordítsa
Bevezetés A Lighttpd az Apache forkja, amely sokkal kevésbé erőforrás-igényes. Könnyű, innen kapta a nevét, és meglehetősen egyszerű a használata. Telepítés
A VULTR a közelmúltban változtatásokat hajtott végre a saját oldalukon, és most már mindennek jól kell működnie, ha a NetworkManager engedélyezve van. Ha szeretné letiltani
Az Icinga2 egy hatékony felügyeleti rendszer, és mester-kliens modellben használva helyettesítheti az NRPE-alapú felügyeleti ellenőrzések szükségességét. A mester-kliens
Más rendszert használ? Az Apache Cassandra egy ingyenes és nyílt forráskódú NoSQL adatbázis-kezelő rendszer, amelyet úgy terveztek, hogy biztosítsa a méretezhetőséget,
Más rendszert használ? A Microweber egy nyílt forráskódú drag and drop CMS és online bolt. A Microweber forráskódja a GitHubon található. Ez az útmutató megmutatja neked
Más rendszert használ? A Vanilla forum egy nyílt forráskódú, PHP-ben írt fórumalkalmazás. Ez egy teljesen testreszabható, könnyen használható, és támogatja a külsőt
Más rendszert használ? A Mattermost egy nyílt forráskódú, saját üzemeltetésű alternatívája a Slack SAAS üzenetküldő szolgáltatásnak. Más szóval, a Mattermost segítségével kb
Mire lesz szüksége Egy Vultr VPS legalább 1 GB RAM-mal. SSH hozzáférés (root/adminisztrátori jogosultságokkal). 1. lépés: A BungeeCord telepítése Először is
A Plesk vezérlőpult nagyon szép integrációt kínál a Lets Encrypt számára. A Lets Encrypt egyike az egyetlen SSL-szolgáltatónak, amely teljes tanúsítványt ad ki
A Lets Encrypt egy tanúsító hatóság, amely ingyenes SSL-tanúsítványokat biztosít. A cPanel ügyes integrációt épített ki, így Ön és ügyfele
Más rendszert használ? A Concrete5 egy nyílt forráskódú CMS, amely számos megkülönböztető és hasznos funkciót kínál, hogy segítse a szerkesztőket a tartalom egyszerű létrehozásában.
Más rendszert használ? A Review Board egy ingyenes és nyílt forráskódú eszköz a forráskód, a dokumentáció, a képek és még sok más áttekintésére. Ez egy web alapú szoftver
Ebből az útmutatóból megtudhatja, hogyan állíthat be HTTP-hitelesítést egy CentOS 7 rendszeren futó Nginx webszerverhez. Követelmények A kezdéshez szüksége lesz a következőre:
Más rendszert használ? A GoAccess egy nyílt forráskódú webnapló-elemző. Használhatja naplók valós idejű elemzésére akár a terminálon, akár a
A YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) egy nyílt forráskódú URL-rövidítő és adatelemző alkalmazás. Ebben a cikkben a telepítés folyamatával foglalkozunk
Más rendszert használ? Bevezetés Az ArangoDB egy nyílt forráskódú NoSQL adatbázis, amely rugalmas adatmodellt kínál dokumentumokhoz, grafikonokhoz és kulcsértékekhez. Ez
Bevezetés Az /etc/ könyvtár kritikus szerepet játszik a Linux rendszer működésében. Ennek az az oka, hogy szinte minden rendszerkonfiguráció
Sok rendszergazda nagy mennyiségű kiszolgálót kezel. Ha a fájlokhoz különböző szervereken keresztül kell hozzáférni, mindegyikbe külön-külön kell bejelentkezni kb
Ez az oktatóanyag végigvezeti Önt a Vultrs rendszerekkel kompatibilis Windows ISO létrehozásának folyamatán. Itt megtanulhatja az <<strong>>Windows ISO<<strong>> előállításának lépéseit az NTLite segítségével.
A mesterséges intelligencia nem a jövőben, hanem itt a jelenben. Ebben a blogban Olvassa el, hogyan hatott a mesterséges intelligencia alkalmazások különböző ágazatokra.
Ön is DDOS támadások áldozata, és tanácstalan a megelőzési módszereket illetően? Olvassa el ezt a cikket a kérdések megoldásához.
Talán hallottál már arról, hogy a hackerek sok pénzt keresnek, de elgondolkodtál már azon, hogyan kereshetnek ennyi pénzt? beszéljük meg.
Szeretné látni a Google forradalmi találmányait, és azt, hogy ezek a találmányok hogyan változtatták meg minden mai ember életét? Ezután olvassa el a blogot, és nézze meg a Google találmányait.
Az önvezető autók koncepciója, hogy mesterséges intelligencia segítségével kerüljenek az utakra, már egy ideje álmunk. De számos ígéret ellenére sehol sem látszanak. Olvassa el ezt a blogot, hogy többet megtudjon…
Ahogy a tudomány gyors ütemben fejlődik, átveszi erőfeszítéseink nagy részét, megnő annak a kockázata is, hogy alávetjük magunkat egy megmagyarázhatatlan szingularitásnak. Olvassa el, mit jelenthet számunkra a szingularitás.
Az adatok tárolási módjai az Adatok születése óta alakulhatnak. Ez a blog egy infografika alapján mutatja be az adattárolás fejlődését.
Olvassa el a blogot, hogy a legegyszerűbb módon ismerje meg a Big Data Architecture különböző rétegeit és azok funkcióit.
Ebben a digitálisan vezérelt világban az intelligens otthoni eszközök az élet döntő részévé váltak. Íme az intelligens otthoni eszközök néhány elképesztő előnye, hogyan teszik életünket érdemessé és egyszerűbbé.