Instal·leu Plesk a CentOS 7
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Plesk és un tauler de control d'amfitrió web propietari que permet als usuaris administrar els seus llocs web personals i/o de clients, bases de dades
H2O és un servidor HTTP de nova generació que té unes excel·lents implementacions HTTP/2 amb totes les funcions de tots els servidors web actuals en ús. Amb H2O com a servidor web, podeu aprofitar les noves característiques de l'especificació HTTP/2, com ara l'optimització de latència, el servidor push i la priorització del costat del servidor que poden aprofitar les funcions modernes del navegador de les quals es parla poc.
En aquest tutorial detallat, us mostraré pas a pas com fer funcionar H2O a la vostra instància CentOS 7 x64.
Inicieu sessió mitjançant SSH amb les credencials que es troben a la vostra instància i actualitzeu el sistema de la següent manera.
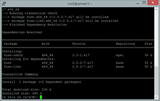
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
Per instal·lar H2O a CentOS 7, heu d'afegir el repositori Bintray RPM per instal·lar els binaris H2O preconstruïts. Utilitzeu l'editor Nano per crear un repositori personalitzat.
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-h2o-rpm.repo
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al fitxer repo.
[bintray-h2o-rpm]
name=bintray-h2o-rpm
baseurl=https://dl.bintray.com/tatsushid/h2o-rpm/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
A continuació, instal·leu H2O.
sudo yum install h2o -y
Ara que H2O està instal·lat, però abans d'habilitar i iniciar el servei, cal una configuració adequada i hem de crear un usuari i un grup específics perquè H2O s'executi. Creeu un grup i un usuari perquè H2O s'executi sota named h2o.
sudo groupadd -g 101 h2o
sudo useradd -d /etc/h2o -g 101 -M -s /sbin/nologin -u 101 h2o
Els passos següents donaran exemples de configuracions per a diverses configuracions de servidors unencrypted, encrypted, statici dynamic; així com una combinació de tots quatre.
http://www.example.coma la http://example.comconfiguració (pàgines HTML estàtiques, sense PHP).Navegueu al /etc/h2o/directori.
cd /etc/h2o/
Canvieu el nom del valor predeterminat h2o.confa h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Creeu un h2o.conffitxer nou .
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al h2o.conffitxer.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Activeu i inicieu el servidor H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Creeu un valor predeterminat index.htmlutilitzant la plantilla /var/www/htmla l'opció de directori que es file.dirmostra més amunt a /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Ara, obriu el vostre navegador i introduïu el nom de domini del servidor ( example.como www.example.com) per a la vostra instància. Rebeu Unable to connectun This site can’t be reachedmissatge o un missatge? La configuració predeterminada del tallafoc de CentOS no permet les connexions entrants al port http. Executeu el següent per obrir-lo.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Actualitzeu la pàgina al vostre navegador ( F5) i rebreu aquest missatge.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.coma la http://www.example.comconfiguració (pàgines HTML estàtiques, sense PHP).Navegueu al /etc/h2o/directori.
cd /etc/h2o/
Canvieu el nom del valor predeterminat h2o.confa h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Creeu un h2o.conffitxer nou .
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al h2o.conffitxer.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Activeu i inicieu el servidor H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Creeu un index.htmlfitxer per defecte utilitzant la plantilla /var/www/htmla l'opció de directori que file.dirs'indica més amunt a /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Ara, obriu el vostre navegador i introduïu el nom de domini del servidor ( example.como www.example.com) per a la vostra instància. Rebeu Unable to connectun This site can’t be reachedmissatge o un missatge? La configuració predeterminada del tallafoc de CentOS no permet les connexions entrants al port http. Feu el següent per obrir-lo.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Actualitzeu la pàgina al vostre navegador ( F5) i rebreu aquest missatge.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://www.example.coma http://example.com(pàgina dinàmica, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfiguracióNavegueu al /etc/h2o/directori.
cd /etc/h2o/
Canvieu el nom del valor predeterminat h2o.confa h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Creeu un h2o.conffitxer nou .
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al h2o.conffitxer.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://www.example.com To http://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text into the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Per processar PHP, cal instal·lar i configurar el dimoni PHP-FPM 7.1. Per instal·lar una versió de PHP-FPM més recent que la 5.4.x per defecte, s'ha d'instal·lar el repo REMI que conté les versions de PHP 5.6.x, 7.0.x i 7.1.x. Escriviu les ordres següents per instal·lar PHP versió 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navegueu al /etc/opt/remi/php71/directori.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Canvieu el nom del valor predeterminat php-fpm.confa php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Creeu un php-fpm.conffitxer nou .
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al php-fpm.conffitxer.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Canvieu el nom del www.conffitxer predeterminat al php-fpm.ddirectori.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Creeu un www.conffitxer nou .
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al www.conffitxer. Canvieu el vostre pm.max\_childrenperquè coincideixi amb el nombre de CPU d'acord amb la vostra instància VPS.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Canvieu el nom del php.inifitxer predeterminat .
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Creeu un php.inifitxer nou .
sudo nano php.ini
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al nou php.ini file. Canvieu memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesizei date.timezoned'acord amb la vostra instància VPS.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Canvieu la propietat del grup per al /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/directori del apachegrup al h2ogrup.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Creeu un directori on residiran els registres del servidor PHP-FPM.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Activeu i inicieu el servidor PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Activeu i inicieu el servidor H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Creeu un directori on index.phpresidirà el valor predeterminat enumerat per l'opció de directori file.diranterior a /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Creeu un valor predeterminat index.phpamb l' phpinfoordre per provar PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copieu i enganxeu el text següent al index.phpfitxer nou .
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Ara, obriu el vostre navegador i introduïu el nom de domini del servidor ( example.como www.example.com) per a la vostra instància. Rebeu Unable to connectun This site can’t be reachedmissatge o un missatge? La configuració predeterminada del tallafoc de CentOS no permet les connexions entrants al port http. Feu el següent per obrir-lo.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Actualitzeu la pàgina al vostre navegador ( F5) i obtindreu la pàgina d'informació de PHP estàndard.
Això conclou el meu tutorial. Gràcies per llegir.
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Plesk és un tauler de control d'amfitrió web propietari que permet als usuaris administrar els seus llocs web personals i/o de clients, bases de dades
Squid és un popular programa Linux gratuït que us permet crear un servidor intermediari web de reenviament. En aquesta guia, veureu com instal·lar Squid a CentOS per convertir-vos-hi
Introducció Lighttpd és una bifurcació d'Apache destinada a ser molt menys intensiu en recursos. És lleuger, d'aquí el seu nom, i és bastant senzill d'utilitzar. Instal·lant
Recentment, VULTR ha fet canvis al seu extrem, i ara tot hauria de funcionar bé des de la caixa amb NetworkManager habilitat. Si voleu desactivar
Icinga2 és un sistema de supervisió potent i, quan s'utilitza en un model de client mestre, pot substituir la necessitat de controls de monitoratge basats en NRPE. El mestre-client
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Apache Cassandra és un sistema de gestió de bases de dades NoSQL gratuït i de codi obert dissenyat per proporcionar escalabilitat, alta
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Microweber és un CMS d'arrossegar i deixar anar de codi obert i una botiga en línia. El codi font de Microweber està allotjat a GitHub. Aquesta guia us mostrarà
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Vanilla Forum és una aplicació de fòrum de codi obert escrita en PHP. És totalment personalitzable, fàcil d'utilitzar i admet externa
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Mattermost és una alternativa autoallotjada de codi obert al servei de missatgeria Slack SAAS. En altres paraules, amb Mattermost, ca
Què necessitareu Un Vultr VPS amb almenys 1 GB de RAM. Accés SSH (amb privilegis d'arrel/administrador). Pas 1: instal·lació de BungeeCord Primer de tot
El tauler de control de Plesk inclou una integració molt agradable per Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt és un dels únics proveïdors SSL que ofereix certificats complets
Lets Encrypt és una autoritat de certificació dedicada a proporcionar certificats SSL de manera gratuïta. cPanel ha creat una integració perfecta perquè tu i el teu client
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Concrete5 és un CMS de codi obert que ofereix moltes característiques distintives i útils per ajudar els editors a produir continguts fàcilment i
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Review Board és una eina gratuïta i de codi obert per revisar el codi font, la documentació, les imatges i molts més. És un programari basat en web
En aquesta guia, aprendràs a configurar l'autenticació HTTP per a un servidor web Nginx que s'executa a CentOS 7. Requisits Per començar, necessitareu el
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? GoAccess és un analitzador de registres web de codi obert. Podeu utilitzar-lo per analitzar els registres en temps real al terminal o
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) és una aplicació d'anàlisi de dades i escurçament d'URL de codi obert. En aquest article, tractarem el procés d'instal·lació
Utilitzeu un sistema diferent? Introducció ArangoDB és una base de dades NoSQL de codi obert amb un model de dades flexible per a documents, gràfics i claus-valors. És
Introducció El directori /etc/ té un paper crític en el funcionament d'un sistema Linux. La raó d'això és perquè gairebé totes les configuracions del sistema
Molts administradors de sistemes gestionen grans quantitats de servidors. Quan s'hagi d'accedir als fitxers a través de diferents servidors, inicieu sessió a cadascun individualment ca
La Intel·ligència Artificial no està en el futur, és aquí mateix en el present. En aquest bloc Llegiu com les aplicacions d'Intel·ligència Artificial han afectat diversos sectors.
També ets víctima d'atacs DDOS i estàs confós sobre els mètodes de prevenció? Llegiu aquest article per resoldre les vostres consultes.
Potser haureu sentit que els pirates informàtics guanyen molts diners, però us heu preguntat mai com guanyen aquest tipus de diners? anem a discutir.
Vols veure els invents revolucionaris de Google i com aquests invents van canviar la vida de tots els éssers humans actuals? A continuació, llegiu al bloc per veure els invents de Google.
El concepte de cotxes autònoms per sortir a les carreteres amb l'ajuda de la intel·ligència artificial és un somni que tenim des de fa temps. Però malgrat les diverses promeses, no es veuen enlloc. Llegeix aquest blog per saber-ne més...
A mesura que la ciència evoluciona a un ritme ràpid, fent-se càrrec de molts dels nostres esforços, també augmenten els riscos de sotmetre'ns a una singularitat inexplicable. Llegeix, què pot significar per a nosaltres la singularitat.
Els mètodes d'emmagatzematge de les dades que han anat evolucionant poden ser des del naixement de les dades. Aquest bloc tracta l'evolució de l'emmagatzematge de dades a partir d'una infografia.
Llegeix el blog per conèixer de la manera més senzilla les diferents capes de l'Arquitectura Big Data i les seves funcionalitats.
En aquest món digital, els dispositius domèstics intel·ligents s'han convertit en una part crucial de les vides. A continuació, es mostren alguns avantatges sorprenents dels dispositius domèstics intel·ligents sobre com fan que la nostra vida valgui la pena i sigui més senzilla.
Recentment, Apple va llançar macOS Catalina 10.15.4, una actualització de suplements per solucionar problemes, però sembla que l'actualització està causant més problemes que provoquen el bloqueig de les màquines Mac. Llegiu aquest article per obtenir més informació