Instaloni Plesk në CentOS 7
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Plesk është një panel kontrolli i pronarit të hostit në internet që lejon përdoruesit të administrojnë faqet e tyre të internetit personale dhe/ose të klientëve, bazat e të dhënave
LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) është një nga formatet e ndryshme të enkriptimit të diskut të disponueshëm për Linux që është agnostik i platformës. Ky tutorial do t'ju ofrojë ndarje rrënjësore dhe shkëmbimi brenda një vëllimi LVM (Linux Volume Manager) që gjendet brenda një ndarjeje të koduar LUKS. Ky tutorial ju lejon gjithashtu të zhbllokoni ndarjen LUKS nga distanca duke përdorur një demon të thjeshtuar të serverit SSH duke përdorur çdo program klient të pajtueshëm SSH.
Në faqen Deploy Servers , bëni sa më poshtë:
Server Locationseksion.CentOS7nën ISO Libraryskedën e Server Typeseksionit.Server Sizeseksion.Deploy Nowbutonin.Përdorni View Consoleopsionin për të hyrë në shembullin VPS përmes tastierës noVNC.
Zgjidhni Install CentOS Linux 7opsionin.
Shtypni Tabtastin.
Futni textpas në vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quietmënyrë që të duket kështu vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet textdhe shtypni Entertastin.
VPS tani do të nisë në instaluesin e modalitetit të tekstit CentOS. Do të shihni një ekran në tastierën noVNC siç tregohet në imazhin më poshtë.

Përdorni Alt + Right Arrow Keykombinimin për të lundruar në konsolën TTY2 për të shtypur komanda në vijën e komandës.
Shkruani komandat e mëposhtme më poshtë për të krijuar një ndarje që përmban ngarkuesin e nisjes GRUB2, një /bootndarje të pakriptuar dhe një ndarje primare që do të mbajë ndarjen LUKS.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme për të shfaqur paraqitjen e ndarjes.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Më pas, plotësoni rootfsndarjen e emërtuar me të dhëna pseudo të rastësishme. Kjo do të marrë pak më shumë se gjysmë ore për të përfunduar.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
Në CentOS 7, cryptsetupkomandat përdorin shifrën e paracaktuar të aes-xts-plain64, madhësinë e paracaktuar të çelësit prej 256 bit dhe hash-in e paracaktuar të SHA1. Në vend të kësaj, ndarja LUKS do të krijohet me shifrën më të sigurt Serpent, me një madhësi çelësi prej 512 bit dhe me hash Whirlpool.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Futni përgjigjet, kur ju kërkohet me pyetjet e mëposhtme, më pas shtypni Entertastin:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordParalajmërim Kjo do të lejojë hyrjen në rrënjë dhe kopjimin pa një kërkesë fjalëkalimi. Vriteni këtë server SSH pasi të keni marrë /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgskedarin.
Për ruajtje, ruani një kopje të kokës së ndarjes LUKS. Kjo siguron që nëse kreu i ndarjes suaj LUKS është dëmtuar disi, ai mund të rikthehet. Nëse titulli dëmtohet pa një kopje rezervë që funksionon, të dhënat tuaja humbasin përgjithmonë.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
Për të kopjuar /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgskedarin nga serveri, një server SSH duhet të fillojë përkohësisht, duke përdorur kopjen e sigurt të ekzekutueshme scpnë një host të klientit, për ta marrë atë.
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme më poshtë për të gjeneruar çelësat pritës SSH.
sshd-keygen
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme më poshtë për të krijuar /etc/ssh/sshd_configskedarin.
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme më poshtë për të redaktuar /etc/ssh/sshd_configskedarin.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Për të redaktuar skedarin, shtypni Inserttastin dhe përdorni tastet me shigjeta për të lundruar te seksionet e skedarit që kanë nevojë për modifikim.
Në rreshtin e parë, ndryshoni numrin Port 22nga parazgjedhja e 22në një numër të rastësishëm sipas zgjedhjes suaj midis 1025dhe 65535. (Shembull: port 25782)
Lëvizni poshtë te rreshti numër trembëdhjetë, shtypni Endtastin dhe shtypni Entertastin.
Në rreshtin tjetër, shtoni HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_keydhe shtypni Entertastin.
Në rreshtin tjetër, shtoni HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keydhe shtypni Entertastin.
Shtypni Esctastin, shkruani :wqdhe shtypni Entertastin për të ruajtur skedarin.
Ndërfaqja e paracaktuar e rrjetit eth0ka nevojë për një adresë IP. Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme më poshtë për të caktuar adresën IP të listuar për shembullin tuaj në eth0ndërfaqen e rrjetit.
dhclient
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme për të shfaqur adresën IP të caktuar. Adresa IP do të renditet menjëherë pas inetdhe përpara netmask. (Shembull: 192.0.2.1netmask inet )
ifconfig eth0
Shkruani komandën e mëposhtme për të nisur serverin SSH.
/usr/sbin/sshd
Nëse përdorni scpkomandën nga një linjë komande në një makinë klienti, përdorni komandën e mëposhtme më poshtë si një shabllon për të marrë /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgskedarin. Zëvendësojeni 25782me numrin aktual të portit të caktuar në /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Zëvendësojeni 192.0.2.1me adresën IP aktuale të caktuar.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
Pas rikthimit të luks-header-backup.imgskedarit, vrasni menjëherë serverin SSH duke shtypur komandën më poshtë në dritaren e konsolës noVNC.
killall sshd
Hapni ndarjen LUKS në mënyrë që të konfiguroni vëllimin fizik LVM që do të jetë brenda.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Input the passphrase created earlier to open the LUKS partition when prompted, then press the Enter key.
Enter passphrase for /dev/vda3: strong-password
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named centos, control, live-base and live-rw. The centos is the LUKS partition.
Type the following command below to create the LVM physical volume.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Type the following command below to create the LVM volume group.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for a swap partition. Use sound judgment to create a swap partition, of the necessary size (-L = size of the volume), based on your VPS instance.
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "swap" created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for the root partition. This will use the remaining free space while reserving five percent (5%) to contain LVM snapshots of your logical volumes if you so choose.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "root" created
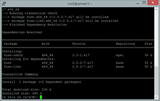
Display the LVM physical volume.
pvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM volume group.
vgdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM logical volume(s).
lvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Type the following command below to deactivate the LVM volume group. This must be completed in order to allow cryptsetup to close the LUKS partition in the next step.
vgchange -a n
When successful, you will receive the following message:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Close the LUKS volume.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
Në sistemet e klientëve tuaj, referojuni seksioneve 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelydhe 3.4. Unlocking using thezhbllokoni commandfaqen Dracut-Crypt-SSH GitHub për të detyruar një kërkesë për frazën e kalimit ose për të përdorur unlockkomandën për të hapur ndarjen tuaj LUKS nga klienti juaj SSH.
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Plesk është një panel kontrolli i pronarit të hostit në internet që lejon përdoruesit të administrojnë faqet e tyre të internetit personale dhe/ose të klientëve, bazat e të dhënave
Squid është një program i popullarizuar, falas Linux që ju lejon të krijoni një përfaqësues në ueb përcjellës. Në këtë udhëzues, do të shihni se si të instaloni Squid në CentOS për t'ju kthyer
Hyrje Lighttpd është një fork i Apache që synon të jetë shumë më pak intensiv me burime. Është i lehtë, prandaj emri i tij, dhe është mjaft i thjeshtë për t'u përdorur. Instaloni
VULTR kohët e fundit ka bërë ndryshime në fund të tyre dhe gjithçka duhet të funksionojë mirë tani me NetworkManager të aktivizuar. Nëse dëshironi të çaktivizoni
Icinga2 është një sistem i fuqishëm monitorimi dhe kur përdoret në një model master-klient, ai mund të zëvendësojë nevojën për kontrolle monitorimi të bazuara në NRPE. Master-klien
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Apache Cassandra është një sistem i menaxhimit të bazës së të dhënave NoSQL falas dhe me burim të hapur që është krijuar për të ofruar shkallëzim, të lartë
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Microweber është një CMS me burim të hapur drag and drop dhe dyqan online. Kodi burimor Microweber është pritur në GitHub. Ky udhëzues do t'ju tregojë
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Mattermost është një alternativë me burim të hapur, të vetë-strehuar për shërbimin e mesazheve Slack SAAS. Me fjalë të tjera, me Mattermost, ju rreth
Paneli i kontrollit Plesk përmban një integrim shumë të bukur për Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt është një nga ofruesit e vetëm SSL që jep plotësisht certifikata
Lets Encrypt është një autoritet certifikimi i dedikuar për të ofruar certifikata SSL pa pagesë. cPanel ka ndërtuar një integrim të pastër në mënyrë që ju dhe klienti juaj
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Concrete5 është një CMS me burim të hapur që ofron shumë veçori dalluese dhe të dobishme për të ndihmuar redaktorët në prodhimin e përmbajtjes me lehtësi dhe
Using a Different System? Review Board is a free and open source tool for reviewing source code, documentation, images and many more. It is web-based softwar
Në këtë udhëzues, do të mësoni se si të konfiguroni vërtetimin HTTP për një server ueb Nginx që funksionon në CentOS 7. Kërkesat Për të filluar, do t'ju duhet
YOURLS (Shkurtësi juaj i URL-së) është një aplikacion për shkurtimin e URL-ve me burim të hapur dhe analitikë të të dhënave. Në këtë artikull, ne do të mbulojmë procesin e instalimit
Përdorimi i një sistemi të ndryshëm? Hyrje ArangoDB është një bazë të dhënash NoSQL me burim të hapur me një model fleksibël të dhënash për dokumente, grafikë dhe vlera-kyçe. Eshte
Hyrje Drejtoria /etc/ luan një rol kritik në mënyrën se si funksionon një sistem Linux. Arsyeja për këtë është sepse pothuajse çdo konfigurim i sistemit
Shumë administratorë të sistemit menaxhojnë sasi të mëdha serverash. Kur skedarët duhet të aksesohen nëpër serverë të ndryshëm, hyni në secilin individualisht rreth
Ky tutorial do të mbulojë procesin e instalimit të një serveri lojërash Half Life 2 në Sistemin CentOS 6. Hapi 1: Instalimi i parakushteve Për të vendosur ou
Laravel GitScrum, ose GitScrum është një mjet produktiviteti me burim të hapur i krijuar për të ndihmuar ekipet e zhvillimit të zbatojnë metodologjinë Scrum në një mënyrë të ngjashme.
Hyrje Në këtë tutorial të Vultr, do të mësoni se si të instaloni PowerDNS. PowerDNS është një program për ekzekutimin e serverëve tuaj të emrave. Është shumë e dobishme kur
Inteligjenca Artificiale nuk është në të ardhmen, është këtu në të tashmen Në këtë blog Lexoni se si aplikacionet e inteligjencës artificiale kanë ndikuar në sektorë të ndryshëm.
A jeni edhe ju viktimë e Sulmeve DDOS dhe jeni konfuz në lidhje me metodat e parandalimit? Lexoni këtë artikull për të zgjidhur pyetjet tuaja.
Ju mund të keni dëgjuar se hakerët fitojnë shumë para, por a keni menduar ndonjëherë se si i fitojnë ato para? Le te diskutojme.
Dëshironi të shihni shpikjet revolucionare nga Google dhe se si këto shpikje ndryshuan jetën e çdo njeriu sot? Më pas lexoni në blog për të parë shpikjet nga Google.
Koncepti i makinave vetë-drejtuese për të dalë në rrugë me ndihmën e inteligjencës artificiale është një ëndërr që e kemi prej kohësh. Por, pavarësisht nga disa premtime, ato nuk shihen askund. Lexoni këtë blog për të mësuar më shumë…
Ndërsa Shkenca evoluon me një ritëm të shpejtë, duke marrë përsipër shumë nga përpjekjet tona, rriten edhe rreziqet për t'iu nënshtruar një Singulariteti të pashpjegueshëm. Lexoni, çfarë mund të thotë singulariteti për ne.
Metodat e ruajtjes së të dhënave kanë evoluar mund të jenë që nga lindja e të dhënave. Ky blog mbulon evolucionin e ruajtjes së të dhënave në bazë të një infografike.
Lexoni blogun për të njohur shtresat e ndryshme në arkitekturën e të dhënave të mëdha dhe funksionalitetet e tyre në mënyrën më të thjeshtë.
Në këtë botë të drejtuar nga dixhitali, pajisjet inteligjente të shtëpisë janë bërë një pjesë thelbësore e jetës. Këtu janë disa përfitime të mahnitshme të pajisjeve shtëpiake inteligjente se si ato e bëjnë jetën tonë të vlefshme dhe më të thjeshtë.
Së fundmi Apple lëshoi macOS Catalina 10.15.4 një përditësim shtesë për të rregulluar problemet, por duket se përditësimi po shkakton më shumë probleme që çojnë në bricking të makinerive mac. Lexoni këtë artikull për të mësuar më shumë