Install Plesk on CentOS 7
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) je jedným z rôznych formátov šifrovania diskov dostupných pre Linux, ktorý je agnostický pre platformu. Tento tutoriál vám poskytne koreňové a odkladacie oddiely vo vnútri zväzku LVM (Linux Volume Manager), ktorý sa nachádza vo vnútri šifrovaného oddielu LUKS. Tento tutoriál vám tiež umožňuje odomknúť oddiel LUKS na diaľku pomocou zjednodušeného démona servera SSH pomocou ľubovoľného kompatibilného klientskeho programu SSH.
Na stránke Nasadiť servery vykonajte nasledovné:
Server Locationsekcii vyberte umiestnenie servera .CentOS7na ISO Librarykarte Server Typesekcie.Server Size.Deploy Nowtlačidlo.Použite View Consolemožnosť prístupu k inštancii VPS cez konzolu noVNC.
Vyberte Install CentOS Linux 7možnosť.
Stlačte Tabkláves .
Zadajte textpotom vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet, aby to vyzeralo takto vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=CentOS\x207\x20\86_64 quiet texta stlačte Enterkláves.
VPS sa teraz spustí do inštalačného programu CentOS v textovom režime. V konzole noVNC uvidíte obrazovku ako na obrázku nižšie.

Pomocou tejto Alt + Right Arrow Keykombinácie prejdite na konzolu TTY2 a zadajte príkazy do príkazového riadku.
Zadajte nasledujúce príkazy nižšie, aby ste vytvorili oddiel, ktorý bude obsahovať zavádzač GRUB2, nezašifrovaný /bootoddiel a primárny oddiel, ktorý bude obsahovať oddiel LUKS.
parted -a opt -s /dev/vda mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vda unit mb
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 1 3
parted -s /dev/vda name 1 grub
parted -s /dev/vda set 1 bios_grub on
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 3 259
parted -s /dev/vda name 2 boot
parted -s /dev/vda mkpart primary 259 100%
parted -s /dev/vda name 3 root
Ak chcete zobraziť rozloženie oddielov, zadajte nasledujúci príkaz.
parted -s /dev/vda print
Ďalej vyplňte pomenovanú rootfsoblasť pseudonáhodnými údajmi. Dokončenie bude trvať niečo vyše pol hodiny.
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vda3 bs=1M status=progress
V systéme CentOS 7 cryptsetuppríkazy používajú predvolenú šifru aes-xts-plain64, predvolenú veľkosť kľúča 256 bitov a predvolenú hodnotu hash SHA1. Namiesto toho bude oblasť LUKS vytvorená pomocou bezpečnejšej šifry Serpent, s veľkosťou kľúča 512 bitov a s hashom Whirlpool.
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/vda3 -c serpent-xts-plain64 -h whirlpool -s 512
Po výzve s nasledujúcimi otázkami zadajte odpovede a potom stlačte Enterkláves:
YESstrong-passwordstrong-passwordUpozornenie Toto umožní rootovské prihlásenie a kopírovanie bez výzvy na zadanie hesla. Po získaní /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgsúboru zabite tento server SSH .
Pre úschovu si uložte kópiu hlavičky partície LUKS. To zaisťuje, že ak je hlavička vašej partície LUKS nejako poškodená, bude možné ju obnoviť. Ak je hlavička poškodená bez fungujúcej zálohy, vaše dáta sú navždy stratené.
cryptsetup luksHeaderBackup /dev/vda3 --header-backup-file /tmp/luks-header-backup.img
Ak chcete skopírovať /tmp/luks-header-backup.imgsúbor zo servera, musí byť dočasne spustený server SSH s použitím zabezpečenej kópie spustiteľného scpna hostiteľskom počítači klienta, aby sa súbor získal.
Zadajte nasledujúci príkaz nižšie na vygenerovanie hostiteľských kľúčov SSH.
sshd-keygen
Zadajte nasledujúci príkaz nižšie na vytvorenie /etc/ssh/sshd_configsúboru.
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config.anaconda /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Ak chcete /etc/ssh/sshd_configsúbor upraviť, zadajte nasledujúci príkaz .
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
To edit the file, press the Insert key and use the arrow keys to navigate to sections of the file that need editing.
In line one, change the number in Port 22 from the default of 22 to a random number of your choice between 1025 and 65535. (Example: port 25782)
Scroll down to line number thirteen, press the End key and press the Enter key.
On the next line, add HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key and press the Enter key.
On the next line, add HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key and press the Enter key.
Press the Esc key, type :wq and press the Enter key to save the file.
The default network interface eth0 needs an IP address. Type the following command below to assign the IP address listed for your instance to the eth0 network interface.
dhclient
Type the following command to display the assigned IP address. The IP address will be listed immediately after inet and before netmask. (Example: inet 192.0.2.1 netmask)
ifconfig eth0
Type the following command to start the SSH server.
/usr/sbin/sshd
If using the scp command from a command line on a client machine, use the following command below as a template to retrieve the /tmp/luks-header-backup.img file. Replace 25782 with the actual port number assigned in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Replace 192.0.2.1 with the actual assigned IP address.
scp -P 25782 [email protected]:/tmp/luks-header-backup.img .
After the retrieval of luks-header-backup.img file, immediately kill the SSH server by typing the command below in the noVNC console window.
killall sshd
Open the LUKS partition in order to set up the LVM physical volume that will reside inside.
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/vda3 centos
Input the passphrase created earlier to open the LUKS partition when prompted, then press the Enter key.
Enter passphrase for /dev/vda3: strong-password
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named centos, control, live-base and live-rw. The centos is the LUKS partition.
Type the following command below to create the LVM physical volume.
pvcreate /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Physical volume "/dev/mapper/centos" successfully created
Type the following command below to create the LVM volume group.
vgcreate ssd /dev/mapper/centos
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Volume group "ssd" successfully created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for a swap partition. Use sound judgment to create a swap partition, of the necessary size (-L = size of the volume), based on your VPS instance.
lvcreate -L 1G -n swap ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "swap" created
Type the following command below to create a LVM logical volume for the root partition. This will use the remaining free space while reserving five percent (5%) to contain LVM snapshots of your logical volumes if you so choose.
lvcreate -l 95%FREE -n root ssd
When successful, you will receive the following message:
Logical volume "root" created
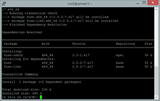
Display the LVM physical volume.
pvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM volume group.
vgdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Display the LVM logical volume(s).
lvdisplay
You will see text in the noVNC console similar to what is pictured in the image below.

Type the following command below to deactivate the LVM volume group. This must be completed in order to allow cryptsetup to close the LUKS partition in the next step.
vgchange -a n
When successful, you will receive the following message:
0 logical volume(s) in volume group "ssd" now active
Close the LUKS volume.
cryptsetup luksClose centos
Type the following command below:
ls /dev/mapper
It will contain the following files named control, live-base and live-rw. The centos file, containing the LUKS partition, will be missing to ensure that that it was closed properly.
Type reboot and press the Enter key to reboot.
Select the Install CentOS Linux 7 option and press the Enter key.
The VPS will now boot into the GUI mode CentOS installer. You will see a screen in the noVNC console like pictured in the image below. Select Install CentOS 7 (1) and press the Enter key.

On the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Continue button (1).

Attention If you're not using the default language of English and the locale of the United States, input your language in the search bar (1). Click on the language (2) and the appropriate locale (3) associated with it. When satisfied, click the blue Continue button (4).

On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY screen, click on INSTALLATION DESTINATION (Automatic partitioning selected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen, select the I will configure partitioning (1) option under Other Storage Options (Partitioning) and click the blue Done button (2) at the top left of the screen.

On the MANUAL PARTITIONING screen, click on the Unknown expandable accordion (1). It will reveal three partitions named BIOS Boot (vda1), Unknown (vda2) and Encrypted (LUKS) (vda3).

With the BIOS Boot partition highlighted in blue (1), select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion and click the Update Settings button (3).

Click on the Unknown partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select ext2 in the File System: accordion (3), enter /boot in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter boot in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Encrypted (LUKS) partition (1) so that it is highlighted in blue. Enter the passphrase you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption in the Passphrase: text field (2) and click the Unlock button (3).

A new Unknown expandable accordion (1) will appear. It will reveal two partitions named Unknown (ssd-root) and Unknown (ssd-swap).

With the Unknown (ssd-root) partition (1) highlighted in blue, select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select xfs in the File System: accordion (3), enter / in the text field (4) under Mount Point:, enter root in the text field (5) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (6).

Click on the Unknown (ssd-swap) (1) partition so that it is highlighted in blue. Select the checkbox option of Reformat (2) next to the File System: accordion. Select swap in the File System: accordion (3), enter swap in the text field (4) under Label: and click the Update Settings button (5).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

A box named SUMMARY OF CHANGES will pop up. Click the Accept Changes button (1). This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

Click on NETWORK & HOST NAME (Not connected) (1) under SYSTEM.

On the NETWORK & HOST NAME screen, move the slider (1), next to the right of Ethernet(eth0) field, from the OFF position to the ON position. If you want to use a custom hostname instead of the default (192.0.2.1.vultr.com) in the Host name: text box (2), change it. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen.

When you are satisfied with the options on the WELCOME TO CENTOS 7 screen, click the blue Begin Installation button (1).

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on ROOT PASSWORD (Root password is not set) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the ROOT PASSWORD screen, enter a strong password in both the Root Password: (1) and Confirm: (2) text fields. Click the blue Done button (3) at the top left of the screen. This will bring you back to the CONFIGURATION screen.

On the CONFIGURATION screen, click on USER CREATION (No user will be created) (1) under USER SETTINGS.

On the CREATE USER screen, enter your full name in the Full name text field (1), an username in the User name text field (2), a strong password in both the Password (3) and Confirm password (4) text fields. Click on the Advanced... button (5).

A box named ADVANCED USER CONFIGURATION will pop up. In the Add user to the following groups: text field (1) under Group Membership, enter wheel and click the Save Changes button (2).

Click the blue Done button (1) at the top left of the screen.

The post-installation process will now commence. It will take a few minutes to complete. When it is finished, click on the blue Reboot button (1) to reboot your VPS instance.

Navigate back to the VULTR Server Management Screen. Click on the Settings link at the top. Click on Custom ISO on the menu on the left side. On the Custom ISO page, click on the Remove ISO button to unmount the ISO and reboot into your CentOS 7 VPS instance. Click the OK button when prompted and the VPS instance will reboot.
Navigate back to the View Console window to access the VPS instance via the noVNC console. Refresh the window if noVNC has disconnected.
You will be prompted to enter the passphrase (Example: Please enter passphrase for disk primary (luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)!:) you created for LUKS partition in Step 3: Setup LVM On LUKS Full Disk Encryption. Enter the passphrase and press the Enter key.

You will then be presented with the console login prompt. You can now close the noVNC console window.
Log in via SSH with a regular user and update the system as follows.
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
While still logged in as a regular user, type the following commands below to install dracut-crypt-ssh.
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/rbu/dracut-crypt-ssh/repo/epel-7/rbu-dracut-crypt-ssh-epel-7.repo
sudo yum install dracut-crypt-ssh -y
Type the following command below to install the nano editor to ease editing of files.
sudo yum install nano -y
You will need to edit the default grub file located in /etc/default/grub.
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Insert rd.neednet=1 ip=dhcp between GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto and rd.luks.uuid=luks-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Save the file by entering the following keyboard combinations. Press the Ctrl + x keys, press the y key and press the Enter key.
Regenerate you GRUB configuration file by type the command below.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
Backup the original /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf by typing the following command below.
sudo mv /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf.orig
Create a new /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf file by typing the following command below.
sudo nano /etc/dracut.conf.d/crypt-ssh.conf
Copy and paste the following text below into the nano editor.
dropbear_acl="/etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys"
dropbear_ecdsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key"
dropbear_rsa_key="/etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key"
Create the directory keys under /etc/dropbear/, with the necessary directory permissions, that will hold the authorized_keys, ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files.
sudo mkdir /etc/dropbear/keys/; sudo chmod /etc/dropbear/keys/
Generate the ssh_ecdsa_key and ssh_rsa_key files with the ssh_keygen program by typing the following commands below. Press the Enter key twice, for each command, when prompted for passphrases.
sudo ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_ecdsa_key
sudo ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/dropbear/keys/ssh_rsa_key
Change the file permissions on ssh_ecdsa_key, ssh_ecdsa_key.pub, ssh_rsa_key and ssh_rsa_key.pub by typing the command below.
sudo chmod 400 /etc/dropbear/keys/*_key; sudo chmod 444 /etc/dropbear/keys/*.pub
Generate public keys using the How Do I Generate SSH Keys? tutorial, found at the beginning of the tutorial under Prerequisites, for your prospective client operating system.
Copy and paste all the text in the public key into the /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys file using the nano program by typing the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dropbear/keys/authorized_keys
You must first build the initramfs and any subsequent update of the dracut-crypt-ssh configuration. Type the following command below for the initial build of the initramfs.
sudo dracut -f
Once that's complete, your CentOS 7 install is set up to listen for your SSH client to connect and allow you to unlock the LUKS partition using your passphrase. You may now reboot your CentOS 7 instance by typing the command below.
sudo reboot
Na klientskych systémoch, pozri sekcie 3.3. Unlocking the volumes interactivelya 3.4. Unlocking using theodomknúť commandna stránke Dracut-Crypt-SSH GitHub buď vynútiť heslo riadku alebo pomocou unlockpríkazu k otvoreniu LUKS oddiel z SSH klienta.
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
Squid je populárny bezplatný linuxový program, ktorý vám umožňuje vytvoriť webový proxy server na presmerovanie. V tejto príručke uvidíte, ako nainštalovať Squid na CentOS, aby vás zmenil
Úvod Lighttpd je fork Apache, ktorého cieľom je byť oveľa menej náročný na zdroje. Je ľahký, odtiaľ jeho názov, a jeho použitie je celkom jednoduché. Installin
VULTR nedávno vykonal zmeny na ich konci a všetko by teraz malo fungovať dobre po vybalení so zapnutým NetworkManagerom. Ak chcete deaktivovať
Icinga2 je výkonný monitorovací systém a pri použití v modeli master-client môže nahradiť potrebu monitorovacích kontrol založených na NRPE. Hlavný klient
Používate iný systém? Apache Cassandra je bezplatný a otvorený systém správy databáz NoSQL, ktorý je navrhnutý tak, aby poskytoval škálovateľnosť, vysokú
Používate iný systém? Microweber je open source drag and drop CMS a online obchod. Zdrojový kód Microweber je umiestnený na GitHub. Tento návod vám to ukáže
Používate iný systém? Mattermost je open source, samostatne hosťovaná alternatíva k službe posielania správ Slack SAAS. Inými slovami, s Mattermostom môžete cca
Čo budete potrebovať Vultr VPS s aspoň 1 GB RAM. Prístup SSH (s oprávneniami root/administrátor). Krok 1: Inštalácia BungeeCord Najprv veci
Ovládací panel Plesk obsahuje veľmi peknú integráciu pre Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt je jedným z mála poskytovateľov SSL, ktorí rozdávajú kompletné certifikáty
Lets Encrypt je certifikačná autorita, ktorá sa venuje bezplatnému poskytovaniu certifikátov SSL. cPanel vytvoril úhľadnú integráciu, takže vy a váš klient
Používate iný systém? Concrete5 je open source CMS, ktorý ponúka mnoho charakteristických a užitočných funkcií, ktoré pomáhajú redaktorom jednoducho vytvárať obsah
Používate iný systém? Review Board je bezplatný a otvorený zdrojový nástroj na kontrolu zdrojového kódu, dokumentácie, obrázkov a mnohých ďalších. Je to webový softvér
V tejto príručke sa dozviete, ako nastaviť HTTP autentifikáciu pre webový server Nginx spustený na CentOS 7. Požiadavky Na začiatok budete potrebovať
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) je open source aplikácia na skrátenie adresy URL a analýzu údajov. V tomto článku sa budeme zaoberať procesom inštalácie
Používate iný systém? Úvod ArangoDB je open source databáza NoSQL s flexibilným dátovým modelom pre dokumenty, grafy a hodnoty kľúča. to je
Úvod Adresár /etc/ hrá rozhodujúcu úlohu v spôsobe fungovania systému Linux. Dôvodom je skutočnosť, že takmer každá konfigurácia systému
Mnoho systémových administrátorov spravuje veľké množstvo serverov. Keď je potrebné pristupovať k súborom cez rôzne servery, prihlásenie do každého z nich samostatne ca
Tento tutoriál sa bude zaoberať procesom inštalácie herného servera Half Life 2 na systém CentOS 6. Krok 1: Inštalácia predpokladov Aby ste mohli nastaviť ou
Laravel GitScrum alebo GitScrum je nástroj na zvýšenie produktivity s otvoreným zdrojom určený na pomoc vývojovým tímom implementovať metodiku Scrum podobným spôsobom.
Umelá inteligencia nie je v budúcnosti, je tu priamo v súčasnosti V tomto blogu si prečítajte, ako aplikácie umelej inteligencie ovplyvnili rôzne sektory.
Ste aj vy obeťou DDOS útokov a máte zmätok ohľadom metód prevencie? Ak chcete vyriešiť svoje otázky, prečítajte si tento článok.
Možno ste už počuli, že hackeri zarábajú veľa peňazí, ale premýšľali ste niekedy nad tým, ako môžu zarábať také peniaze? poďme diskutovať.
Chcete vidieť revolučné vynálezy od Google a ako tieto vynálezy zmenili život každého dnešného človeka? Potom si prečítajte na blogu a pozrite si vynálezy spoločnosti Google.
Koncept samoriadených áut vyraziť na cesty s pomocou umelej inteligencie je snom, ktorý máme už nejaký čas. Ale napriek niekoľkým prísľubom ich nikde nevidno. Prečítajte si tento blog a dozviete sa viac…
Ako sa veda vyvíja rýchlym tempom a preberá veľa nášho úsilia, zvyšuje sa aj riziko, že sa vystavíme nevysvetliteľnej singularite. Prečítajte si, čo pre nás môže znamenať singularita.
Spôsoby ukladania údajov sa môžu vyvíjať už od zrodu údajov. Tento blog sa zaoberá vývojom ukladania údajov na základe infografiky.
Prečítajte si blog, aby ste čo najjednoduchším spôsobom spoznali rôzne vrstvy architektúry veľkých dát a ich funkcie.
V tomto digitálnom svete sa inteligentné domáce zariadenia stali kľúčovou súčasťou života. Tu je niekoľko úžasných výhod inteligentných domácich zariadení o tom, ako robia náš život, ktorý stojí za to žiť, a ktorý zjednodušujú.
Spoločnosť Apple nedávno vydala doplnkovú aktualizáciu macOS Catalina 10.15.4 na opravu problémov, ale zdá sa, že táto aktualizácia spôsobuje ďalšie problémy, ktoré vedú k blokovaniu počítačov Mac. Prečítajte si tento článok a dozviete sa viac