Install Plesk on CentOS 7
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
Buildbot je open source nástroj na nepretržitú integráciu založený na Pythone na automatizáciu tvorby, testovania a nasadzovania softvéru. Buildbot pozostáva z jedného alebo viacerých Buildbot master a niekoľkých pracovníkov. Buildbot master alebo Buildmaster má centrálne riadenie systému. Je zodpovedný za riadenie prostredia stavby, pracovníkov a robí všetky rozhodnutia o posielaní pracovných miest pracovníkom. Buildmaster zisťuje zmeny v úložisku kódu a odosiela príkazy alebo úlohy pracovníkom na vykonanie. Pracovníci vykonajú úlohy a vrátia výsledok Buildmasterovi. Buildmaster potom informuje vývojárov prostredníctvom viacerých podporovaných kanálov. V tomto návode nainštalujeme Buildbot master and worker na CentOS 7. Nakonfigurujeme aj autentifikáciu a Nginx ako zabezpečenú reverznú proxy.
V tomto návode budeme používať 192.168.1.1ako verejnú IP adresu a ci.example.comako názov domény smerujúci k inštancii Vultr. Uistite sa, že ste nahradili všetky výskyty vzorového názvu domény a adresy IP skutočnými.
Aktualizujte svoj základný systém pomocou príručky Ako aktualizovať CentOS 7 . Po aktualizácii vášho systému pokračujte v inštalácii PostgreSQL.
Nainštalujte Pip, čo je správca balíkov pre Python.
sudo yum -y install epel-release
sudo yum -y install python-pip gcc python-devel git
sudo pip install --upgrade pip
Buildbot podporuje viacero typov databázových serverov, ako sú MySQL, PostgreSQL a SQLite. V tomto návode použijeme PostgreSQL na hosťovanie databázového servera Buildbot.
PostgreSQL je objektovo-relačný databázový systém známy svojou stabilitou a rýchlosťou. Predvolené yumúložisko obsahuje starú verziu PostgreSQL, preto pridajte úložisko PostgreSQL.
sudo yum -y install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/10/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos10-10-1.noarch.rpm
Nainštalujte databázový server PostgreSQL.
sudo yum -y install postgresql10-server postgresql10-contrib postgresql10
Inicializujte databázu.
sudo /usr/pgsql-10/bin/postgresql-10-setup initdb
Spustite server PostgreSQL a povoľte jeho automatické spustenie pri štarte.
sudo systemctl start postgresql-10
sudo systemctl enable postgresql-10
Zmeňte heslo pre predvoleného používateľa PostgreSQL.
sudo passwd postgres
Prihláste sa ako používateľ PostgreSQL.
sudo su - postgres
Vytvorte nového používateľa PostgreSQL pre Buildbot.
createuser bb_user
Ak chcete, môžete namiesto mena použiť ľubovoľné používateľské meno bb_user. PostgreSQL poskytuje psqlshell na spúšťanie dotazov v databáze. Prepnite sa do prostredia PostgreSQL.
psql
Nastavte heslo pre novo vytvoreného používateľa.
ALTER USER bb_user WITH ENCRYPTED password 'DBPassword';
Nahraďte DBPasswordho bezpečným heslom.
Vytvorte novú databázu pre inštaláciu Buildbot.
CREATE DATABASE buildbot OWNER bb_user;
Vyjdite z psqlulity.
\q
Prepnúť na sudopoužívateľa.
exit
Upravte pg_hba.confsúbor, aby ste povolili autentifikáciu založenú na MD5.
sudo nano /var/lib/pgsql/10/data/pg_hba.conf
Nájdite nasledujúce riadky a zmeňte hodnoty peera identv METHODstĺpci na trusta md5.
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all peer
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 ident
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 ident
Po aktualizácii bude konfigurácia vyzerať ako nasledujúci text.
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all trust
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 md5
Uložte súbor a ukončite editor. Nainštalujte databázový adaptér PostgreSQL pre Python.
sudo pip install psycopg2
Reštartujte PostgreSQL, aby sa zmeny prejavili.
sudo systemctl restart postgresql-10
Nainštalujte Buildbot pomocou Pip.
sudo pip install 'buildbot[bundle]' pyopenssl service_identity
Vyššie uvedený príkaz nainštaluje Buildbot spolu s buildbot-www, buildbot-worker, a niekoľkými webovými zásuvnými modulmi, ako napríklad buildbot-waterfall-view.
Aby ste sa uistili, že Buildbot bol úspešne nainštalovaný, môžete to overiť kontrolou verzie Buildbot.
buildbot --version
Výstup by mal pripomínať nasledujúci text.
[user@vultr ~]$ buildbot --version
Buildbot version: 0.9.15.post1
Twisted version: 17.9.0
Modify your firewall rules to allow port 8010. Buildbot uses this port to listen to the web requests.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8010/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Create a new unprivileged user to run Buildbot master and worker processes. It is not recommended to run Buildbot master services as the root user.
sudo adduser buildbot
sudo passwd buildbot
Log in as the newly created buildbot user.
sudo su - buildbot
Set up the Buildbot master in /home/buildbot/master directory. This directory will contain the configuration, status and log files of each build.
buildbot create-master --db 'postgresql://bb_user:DBPassword@localhost/buildbot' ~/master
Make sure to replace the credentials of the database user in the above command.
Note: If you wish to use SQLite database instead of PostgreSQL, simply omit the --db 'postgresql://bb_user:DBpassword@localhost/buildbot' option. The SQLite database will be created in the same directory.
The above command will create the ~/master directory to store the Buildmaster files. It will also write the data into the PostgreSQL database. You will get the following output.
[buildbot@vultr ~]$ buildbot create-master --db 'postgresql://bb_user:DBPassword@localhost/buildbot' ~/master
mkdir /home/buildbot/master
creating /home/buildbot/master/master.cfg.sample
creating database (postgresql://bb_user:DBPassword@localhost/buildbot)
buildmaster configured in /home/buildbot/master
Copy the sample configuration file to a live configuration file.
cp ~/master/master.cfg.sample ~/master/master.cfg
Edit the configuration file.
nano ~/master/master.cfg
Find the following lines.
c['workers'] = [worker.Worker("example-worker", "pass")]
...
c['builders'].append(
util.BuilderConfig(name="runtests",
workernames=["example-worker"],
factory=factory))
...
c['title'] = "Hello World CI"
c['titleURL'] = "https://buildbot.github.io/hello-world/"
...
c['buildbotURL'] = "http://localhost:8010/"
...
c['db'] = {
'db_url' : "postgresql://bb_user:DBpassword@localhost/buildbot",
}
The above configuration has an entry for a sample worker. We will modify the sample entry for the worker we will be running on localhost. Change the example-worker to any suitable name for the localhost worker and change the pass to some other password. Make a note of the worker name and password as we will require that later in the tutorial. Change the name of the worker in the list of builders. Change the name of the application and project URL according to your needs.
Change the Buildbot URL from localhost to your actual domain name or public IP address. Also, verify that the database information in the configuration file matches your actual database credentials.
At the end of the file, add c['buildbotNetUsageData'] = None. This parameter will disable sending the software version information and plugin usage details to the developers. However, to enable sending the uses information, change the option to Full.
The configuration should look like the following text.
c['workers'] = [worker.Worker("localhost-worker", "Password123")]
...
c['builders'].append(
util.BuilderConfig(name="runtests",
workernames=["localhost-worker"],
factory=factory))
...
c['title'] = "My Application CI"
c['titleURL'] = "https://example.com/my-app"
...
c['buildbotURL'] = "http://192.168.1.1:8010/"
...
c['db'] = {
'db_url' : "postgresql://bb_user:DBpassword@localhost/buildbot",
}
...
c['buildbotNetUsageData'] = None
Save the file and exit the editor. Check the configuration file for errors.
buildbot checkconfig ~/master
If the configuration file has no errors, you will see following output.
[buildbot@vultr ~]$ buildbot checkconfig ~/master
Config file is good!
Now that everything is configured correctly, you can start the Buildbot master.
buildbot start ~/master
You will see the following output.
[buildbot@vultr ~]$ buildbot start ~/master
Following twistd.log until startup finished..
The buildmaster appears to have (re)started correctly.
Now that the Buildbot master has started correctly, the web user interface is accessible at http://192.168.1.1:8010. You should see the following Buildbot interface.

Since we have already modified the worker configuration in ~/master/master.cfg, we can proceed to create a new worker.
buildbot-worker create-worker ~/worker localhost localhost-worker Password123
Make sure that you use the exact same worker name and password as mentioned in ~/master/master.cfg file. If there's a mismatch in worker name or password, the worker will not be able to connect to the Buildbot master. You will see the following output upon successful execution.
[buildbot@vultr ~]$ buildbot-worker create-worker ~/worker localhost example-worker pass
mkdir /home/buildbot/worker
mkdir /home/buildbot/worker/info
Creating info/admin, you need to edit it appropriately.
Creating info/host, you need to edit it appropriately.
Not creating info/access_uri - add it if you wish
Please edit the files in /home/buildbot/worker/info appropriately.
worker configured in /home/buildbot/worker
Information about the worker is stored in the /info directory. Edit the administrative information about the developer.
nano ~/worker/info/admin
Replace the example name with your actual name and email.
Your Name <[email protected]>
Now, open the file containing information about the host.
nano ~/worker/info/host
Replace the example instruction with the actual information about the host system.
Localhost, CentOS 7
The worker admin and host information is only used to tell the users about the system. You can also add additional information about the system such as Buildbot version and Twisted version.
Start the worker.
buildbot-worker start ~/worker
The output will look like the following text.
[buildbot@vultr ~]$ buildbot-worker start ~/worker
Following twistd.log until startup finished..
The buildbot-worker appears to have (re)started correctly.
To check if the worker is registered, head to the web interface of Buildbot and navigate to Builds >> Workers from the left navigation. You should see that the worker is up and ready to build.

To run a sample build, to check if the Buildbot worker is running successfully, navigate to Builds >> Builders. Click on the runtests builder name to open the builder interface and click on the Force button to force a build. Provide your name and click on the Start Build button to start the build. Since it is a sample build test to check the Buildbot environment, it will finish in a couple of seconds. You will get a success message and the build result.

Although the Buildbot master and worker can be easily started using the commands above, it is recommended to use Systemd units to run and manage the Buildbot services. This will ensure that they are automatically started on system restart and failures.
Note: Switch to the sudo user again by running either exit or su <username>. From now on all the commands need to be executed by the sudo user.
Stop the running Buildbot worker and master service.
sudo su buildbot -c "buildbot stop /home/buildbot/master"
sudo su buildbot -c "buildbot-worker stop ~/worker"
Create a new Systemd unit file for the Buildbot master.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/buildbot.service
Populate the file.
[Unit]
Description=BuildBot master service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=buildbot
Group=buildbot
WorkingDirectory=/home/buildbot/master
ExecStart=/usr/bin/buildbot start
ExecStop=/usr/bin/buildbot stop
ExecReload=/usr/bin/buildbot restart
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Start the Buildbot master and enable it to automatically start at boot time.
sudo systemctl start buildbot
sudo systemctl enable buildbot
Create a new Systemd unit file for the Buildbot worker.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/buildbot-worker.service
Populate the file.
[Unit]
Description=BuildBot worker service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=buildbot
Group=buildbot
WorkingDirectory=/home/buildbot/worker
ExecStart=/usr/bin/buildbot-worker start
ExecStop=/usr/bin/buildbot-worker stop
ExecReload=/usr/bin/buildbot-worker restart
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Start the Buildbot worker and enable it to automatically start at boot time.
sudo systemctl start buildbot-worker
sudo systemctl enable buildbot-worker
You can check the status of the services.
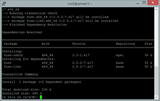
sudo systemctl status buildbot buildbot-worker
If the services are running smoothly, you will see that in the output.
[user@vultr ~]$ sudo systemctl status buildbot buildbot-worker
● buildbot.service - BuildBot master service
...
Active: active (running) since Fri 2018-01-12 16:00:59 UTC; 1min 25s ago
...
Jan 12 16:00:59 vultr.guest systemd[1]: Started BuildBot master service.
● buildbot-worker.service - BuildBot worker service
...
Active: active (running) since Fri 2018-01-12 16:02:00 UTC; 24s ago
...
Jan 12 16:02:00 vultr.guest systemd[1]: Started BuildBot worker service.
By default, authentication is not enabled in the Buildbot web interface. For internet facing sites, it is strongly recommended to setup authentication so that only the authorized users can have the ability to perform administrative tasks. To set up authentication, reopen the Buildbot master configuration file.
sudo su buildbot -c "nano /home/buildbot/master/master.cfg"
Add the following lines to the end of the file.
c['www']['authz'] = util.Authz(
allowRules = [
util.AnyEndpointMatcher(role="admins")
],
roleMatchers = [
util.RolesFromUsername(roles=['admins'], usernames=['admin_user'])
]
)
c['www']['auth'] = util.UserPasswordAuth({'admin_user': 'AdminPassword'})
Replace both occurrences of admin_user with the actual username you want to use and AdminPassword with a strong password.
Check for errors in the configuration file.
sudo su buildbot -c "buildbot checkconfig /home/buildbot/master"
Restart Buildbot master service so that the changes can take effect.
sudo systemctl restart buildbot
Browse the web interface again to see that the anonymous users can only view the basic details about the build server. Now, log in using the credentials set in the master.cfg file and you will see that all other administrative functions are only available to the logged in admin user.
By default, Buildbot listens to the port 8010 on unsecured connections. Securing the web interface with HTTPS is recommended to ensure that the data is safe during transportation from the browser to the server. In this section of the tutorial, we will install and secure Nginx with Let's Encrypt free SSL certificates. The Nginx web server will work as a reverse proxy to forward the incoming requests to Buildbot's HTTP endpoint.
Install Nginx.
sudo yum -y install nginx
Start Nginx and enable it to automatically start at boot time.
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
Install Certbot, which is the client application for Let's Encrypt CA.
sudo yum -y install certbot
Before you can request the certificates, you will need to allow ports 80 and 443 or standard HTTP and HTTPS services through the firewall. Also, remove port 8010, which listens to the unsecured connections.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8010/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Note: To obtain certificates from Let's Encrypt CA, the domain for which the certificates are to be generated must be pointed towards the server. If not, make the necessary changes to the DNS records of the domain and wait for the DNS to propagate before making the certificate request again. Certbot checks the domain authority before providing the certificates.
Generate the SSL certificates.
sudo certbot certonly --webroot -w /usr/share/nginx/html -d ci.example.com
Vygenerované certifikáty budú pravdepodobne uložené v /etc/letsencrypt/live/ci.example.com/adresári. Certifikát SSL bude uložený ako fullchain.pema súkromný kľúč bude uložený ako privkey.pem.
Platnosť certifikátov Let's Encrypt vyprší o 90 dní, preto sa odporúča nastaviť automatické obnovovanie certifikátov pomocou úloh Cron.
Otvorte súbor úlohy cron pre rootpoužívateľa.
sudo crontab -e
Na koniec súboru pridajte nasledujúci riadok.
30 5 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quiet
Vyššie uvedená úloha cron sa spustí každý deň o 5:30. Ak má certifikát vypršať, automaticky ho obnoví.
Teraz zmeňte predvolený konfiguračný súbor Nginx, aby ste odstránili default_serverriadok.
sudo sed -i 's/default_server//g' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Vytvorte nový konfiguračný súbor pre webové rozhranie Buildbot.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/buildbot.conf
Vyplňte súbor.
upstream buildbot {
server 127.0.0.1:8010;
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name ci.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
server_name ci.example.com;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/ci.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/ci.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 1440m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!CAMELLIA:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubdomains;";
access_log /var/log/nginx/buildbot.access.log;
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
location / {
proxy_pass http://buildbot;
}
location /sse/ {
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_pass http://buildbot/sse/;
}
location /ws {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_pass http://buildbot/ws;
proxy_read_timeout 6000s;
}
}
Skontrolujte chyby v novom konfiguračnom súbore.
sudo nginx -t
Ak uvidíte nasledujúci výstup, konfigurácia je bez chýb.
[user@vultr ~]$ sudo nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Ak ste dostali nejaký druh chyby, nezabudnite dvakrát skontrolovať cestu k certifikátom SSL. Reštartujte webový server Nginx, aby ste implementovali zmenu v konfigurácii.
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Otvorte konfiguračný súbor Buildmaster.
sudo su buildbot -c "nano /home/buildbot/master/master.cfg"
Nájdite nasledujúci riadok.
c['buildbotURL'] = "http://192.168.1.1:8010/"
Zmeňte adresu URL podľa názvu domény, ktorú používate.
c['buildbotURL'] = "https://ci.example.com/"
Reštartujte hlavnú službu Buildbot.
sudo systemctl restart buildbot
Teraz máte prístup k hlavnému panelu Buildbot na adrese https://ci.example.com. Uvidíte, že pripojenia k Buildbot sú teraz zabezpečené pomocou SSL.

Prihláste sa pomocou poverení správcu a pridajte svoj prvý kanál, aby ste mohli začať vytvárať svoju aplikáciu.
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
Squid je populárny bezplatný linuxový program, ktorý vám umožňuje vytvoriť webový proxy server na presmerovanie. V tejto príručke uvidíte, ako nainštalovať Squid na CentOS, aby vás zmenil
Úvod Lighttpd je fork Apache, ktorého cieľom je byť oveľa menej náročný na zdroje. Je ľahký, odtiaľ jeho názov, a jeho použitie je celkom jednoduché. Installin
VULTR nedávno vykonal zmeny na ich konci a všetko by teraz malo fungovať dobre po vybalení so zapnutým NetworkManagerom. Ak chcete deaktivovať
Icinga2 je výkonný monitorovací systém a pri použití v modeli master-client môže nahradiť potrebu monitorovacích kontrol založených na NRPE. Hlavný klient
Používate iný systém? Apache Cassandra je bezplatný a otvorený systém správy databáz NoSQL, ktorý je navrhnutý tak, aby poskytoval škálovateľnosť, vysokú
Používate iný systém? Microweber je open source drag and drop CMS a online obchod. Zdrojový kód Microweber je umiestnený na GitHub. Tento návod vám to ukáže
Používate iný systém? Mattermost je open source, samostatne hosťovaná alternatíva k službe posielania správ Slack SAAS. Inými slovami, s Mattermostom môžete cca
Čo budete potrebovať Vultr VPS s aspoň 1 GB RAM. Prístup SSH (s oprávneniami root/administrátor). Krok 1: Inštalácia BungeeCord Najprv veci
Ovládací panel Plesk obsahuje veľmi peknú integráciu pre Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt je jedným z mála poskytovateľov SSL, ktorí rozdávajú kompletné certifikáty
Lets Encrypt je certifikačná autorita, ktorá sa venuje bezplatnému poskytovaniu certifikátov SSL. cPanel vytvoril úhľadnú integráciu, takže vy a váš klient
Používate iný systém? Concrete5 je open source CMS, ktorý ponúka mnoho charakteristických a užitočných funkcií, ktoré pomáhajú redaktorom jednoducho vytvárať obsah
Používate iný systém? Review Board je bezplatný a otvorený zdrojový nástroj na kontrolu zdrojového kódu, dokumentácie, obrázkov a mnohých ďalších. Je to webový softvér
V tejto príručke sa dozviete, ako nastaviť HTTP autentifikáciu pre webový server Nginx spustený na CentOS 7. Požiadavky Na začiatok budete potrebovať
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) je open source aplikácia na skrátenie adresy URL a analýzu údajov. V tomto článku sa budeme zaoberať procesom inštalácie
Používate iný systém? Úvod ArangoDB je open source databáza NoSQL s flexibilným dátovým modelom pre dokumenty, grafy a hodnoty kľúča. to je
Úvod Adresár /etc/ hrá rozhodujúcu úlohu v spôsobe fungovania systému Linux. Dôvodom je skutočnosť, že takmer každá konfigurácia systému
Mnoho systémových administrátorov spravuje veľké množstvo serverov. Keď je potrebné pristupovať k súborom cez rôzne servery, prihlásenie do každého z nich samostatne ca
Tento tutoriál sa bude zaoberať procesom inštalácie herného servera Half Life 2 na systém CentOS 6. Krok 1: Inštalácia predpokladov Aby ste mohli nastaviť ou
Laravel GitScrum alebo GitScrum je nástroj na zvýšenie produktivity s otvoreným zdrojom určený na pomoc vývojovým tímom implementovať metodiku Scrum podobným spôsobom.
Umelá inteligencia nie je v budúcnosti, je tu priamo v súčasnosti V tomto blogu si prečítajte, ako aplikácie umelej inteligencie ovplyvnili rôzne sektory.
Ste aj vy obeťou DDOS útokov a máte zmätok ohľadom metód prevencie? Ak chcete vyriešiť svoje otázky, prečítajte si tento článok.
Možno ste už počuli, že hackeri zarábajú veľa peňazí, ale premýšľali ste niekedy nad tým, ako môžu zarábať také peniaze? poďme diskutovať.
Chcete vidieť revolučné vynálezy od Google a ako tieto vynálezy zmenili život každého dnešného človeka? Potom si prečítajte na blogu a pozrite si vynálezy spoločnosti Google.
Koncept samoriadených áut vyraziť na cesty s pomocou umelej inteligencie je snom, ktorý máme už nejaký čas. Ale napriek niekoľkým prísľubom ich nikde nevidno. Prečítajte si tento blog a dozviete sa viac…
Ako sa veda vyvíja rýchlym tempom a preberá veľa nášho úsilia, zvyšuje sa aj riziko, že sa vystavíme nevysvetliteľnej singularite. Prečítajte si, čo pre nás môže znamenať singularita.
Spôsoby ukladania údajov sa môžu vyvíjať už od zrodu údajov. Tento blog sa zaoberá vývojom ukladania údajov na základe infografiky.
Prečítajte si blog, aby ste čo najjednoduchším spôsobom spoznali rôzne vrstvy architektúry veľkých dát a ich funkcie.
V tomto digitálnom svete sa inteligentné domáce zariadenia stali kľúčovou súčasťou života. Tu je niekoľko úžasných výhod inteligentných domácich zariadení o tom, ako robia náš život, ktorý stojí za to žiť, a ktorý zjednodušujú.
Spoločnosť Apple nedávno vydala doplnkovú aktualizáciu macOS Catalina 10.15.4 na opravu problémov, ale zdá sa, že táto aktualizácia spôsobuje ďalšie problémy, ktoré vedú k blokovaniu počítačov Mac. Prečítajte si tento článok a dozviete sa viac