Instalirajte Plesk na CentOS 7
Korištenje drugog sustava? Plesk je vlasnička upravljačka ploča web hosta koja omogućuje korisnicima da administriraju svoje osobne i/ili klijentske web stranice, baze podataka
H2O je HTTP poslužitelj nove generacije koji ima sjajnu, potpuno opremljenu HTTP/2 implementaciju svih trenutnih web poslužitelja u upotrebi. Uz H2O kao vaš web poslužitelj, možete iskoristiti prednosti novih značajki HTTP/2 specifikacije, kao što su optimizacija kašnjenja, server-push i prioritet na strani poslužitelja koji mogu iskoristiti prednosti modernih značajki preglednika o kojima se rijetko govori.
U ovom detaljnom vodiču pokazat ću vam korak po korak kako pokrenuti H2O na vašoj CentOS 7 x64 instanci.
Prijavite se putem SSH-a s vjerodajnicama koje se nalaze pod vašom instancom i ažurirajte sustav na sljedeći način.
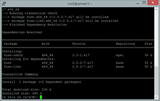
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
Da biste instalirali H2O na CentOS 7, morate dodati spremište Bintray RPM da biste instalirali unaprijed izgrađene H2O binarne datoteke. Upotrijebite Nano uređivač za izradu prilagođenog repo.
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-h2o-rpm.repo
Kopirajte i zalijepite donji tekst u repo datoteku.
[bintray-h2o-rpm]
name=bintray-h2o-rpm
baseurl=https://dl.bintray.com/tatsushid/h2o-rpm/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Zatim instalirajte H2O.
sudo yum install h2o -y
Sada kada je H2O instaliran, ali prije nego što omogućite i pokrenete uslugu, potrebna je ispravna konfiguracija i moramo stvoriti određenog korisnika i grupu pod kojima će H2O raditi. Stvorite grupu i korisnika za H2O pod imenom h2o.
sudo groupadd -g 101 h2o
sudo useradd -d /etc/h2o -g 101 -M -s /sbin/nologin -u 101 h2o
Sljedeći koraci će dati primjere konfiguracijskih postavki za različite postavke unencrypted, encrypted, statici dynamicposlužitelja; kao i kombinacija sva četiri.
http://www.example.comna http://example.com(statičke HTML stranice, bez PHP-a) konfiguracijuIdite do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte zadano h2o.confu h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Napravite novu h2o.confdatoteku.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte i zalijepite donji tekst u h2o.confdatoteku.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Omogućite i pokrenite H2O poslužitelj.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Izradite zadanu vrijednost index.htmlpomoću predloška u gore navedenoj /var/www/htmlopciji direktorija file.diru /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Sada otvorite svoj preglednik i unesite naziv domene poslužitelja ( example.comili www.example.com) za svoju instancu. Dobivate li poruku Unable to connectili This site can’t be reachedporuku? Zadana postavka vatrozida CentOS-a onemogućuje dolazne veze na http port. Izvršite sljedeće da ga otvorite.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvježite stranicu u svom pregledniku ( F5) i dobit ćete ovu poruku.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.comna http://www.example.com(statičke HTML stranice, bez PHP-a) konfiguracijuIdite do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte zadano h2o.confu h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Napravite novu h2o.confdatoteku.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte i zalijepite sljedeći tekst u h2o.confdatoteku.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Omogućite i pokrenite H2O poslužitelj.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Izradite zadanu index.htmldatoteku koristeći predložak u /var/www/htmlopciju direktorija file.dirnavedenu gore u /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Sada otvorite svoj preglednik i unesite naziv domene poslužitelja ( example.comili www.example.com) za svoju instancu. Dobivate li poruku Unable to connectili This site can’t be reachedporuku? Zadana postavka vatrozida CentOS-a onemogućuje dolazne veze na http port. Učinite sljedeće da ga otvorite.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvježite stranicu u svom pregledniku ( F5) i dobit ćete ovu poruku.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://www.example.comna http://example.com(Dinamičku stranicu, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) konfiguracijuIdite do /etc/h2o/imenika.
cd /etc/h2o/
Preimenujte zadano h2o.confu h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Napravite novu h2o.confdatoteku.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Kopirajte i zalijepite sljedeći tekst u h2o.confdatoteku.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://www.example.com To http://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text into the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Da bi se obradio PHP, PHP-FPM 7.1 demon mora biti instaliran i konfiguriran. Da biste instalirali verziju PHP-FPM-a noviju od zadane 5.4.x, mora biti instaliran REMI repo koji sadrži PHP verzije 5.6.x, 7.0.x i 7.1.x. Upišite sljedeće naredbe za instalaciju PHP verzije 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Idite do /etc/opt/remi/php71/imenika.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Preimenujte zadano php-fpm.confu php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Napravite novu php-fpm.confdatoteku.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Kopirajte i zalijepite sljedeći tekst u php-fpm.confdatoteku.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Preimenujte zadanu www.confdatoteku u php-fpm.ddirektoriju.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Napravite novu www.confdatoteku.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Kopirajte i zalijepite donji tekst u www.confdatoteku. Promijenite tako pm.max\_childrenda odgovara broju CPU-a u skladu s vašom VPS instancom.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Preimenujte zadanu php.inidatoteku.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Napravite novu php.inidatoteku.
sudo nano php.ini
Kopirajte i zalijepite sljedeći tekst ispod u novi php.ini file. Promjena memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesizei date.timezone, u skladu sa svojim VPS primjer.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Promijenite vlasništvo grupe za /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/imenik iz apachegrupe u h2ogrupu.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Napravite direktorij u kojem će se nalaziti zapisnici PHP-FPM poslužitelja.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Omogućite i pokrenite PHP-FPM poslužitelj.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Omogućite i pokrenite H2O poslužitelj.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Stvorite direktorij u kojem index.phpće se nalaziti zadana postavka naveden u file.dirgornjoj opciji direktorija u /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Izradite zadano index.phppomoću phpinfonaredbe za testiranje PHP-a.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Kopirajte i zalijepite donji tekst u novu index.phpdatoteku.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Sada otvorite svoj preglednik i unesite naziv domene poslužitelja ( example.comili www.example.com) za svoju instancu. Dobivate li poruku Unable to connectili This site can’t be reachedporuku? Zadana postavka vatrozida CentOS-a onemogućuje dolazne veze na http port. Učinite sljedeće da ga otvorite.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Osvježite stranicu u svom pregledniku ( F5) i dobit ćete standardnu PHP stranicu s informacijama.
Ovim završavam moj tutorijal. Hvala na čitanju.
Korištenje drugog sustava? Plesk je vlasnička upravljačka ploča web hosta koja omogućuje korisnicima da administriraju svoje osobne i/ili klijentske web stranice, baze podataka
Squid je popularan besplatni program za Linux koji vam omogućuje stvaranje web proxyja za prosljeđivanje. U ovom vodiču vidjet ćete kako instalirati Squid na CentOS da vas preokrene
Uvod Lighttpd je fork Apachea koji ima za cilj da bude puno manje intenzivan prema resursima. Lagan je, otuda mu i naziv, i prilično je jednostavan za korištenje. Instaliraj
VULTR je nedavno napravio promjene na svojoj strani i sada bi sve trebalo raditi dobro iz kutije s omogućenim NetworkManagerom. Želite li onemogućiti
Icinga2 je moćan sustav nadzora, a kada se koristi u modelu master-client, može zamijeniti potrebu za provjerama praćenja na temelju NRPE. Glavni klijent
Korištenje drugog sustava? Apache Cassandra je besplatni i otvorenog koda NoSQL sustav upravljanja bazom podataka koji je osmišljen kako bi osigurao skalabilnost, visoku
Korištenje drugog sustava? Microweber je CMS i internetska trgovina otvorenog koda povuci i ispusti. Izvorni kod Microwebera nalazi se na GitHubu. Ovaj vodič će vam pokazati
Korištenje drugog sustava? Mattermost je open source alternativa Slack SAAS servisu za razmjenu poruka. Drugim riječima, s Mattermostom možete ca
Što vam treba Vultr VPS s najmanje 1 GB RAM-a. SSH pristup (s root/administrativnim privilegijama). Korak 1: Instalacija BungeeCord-a Najprije
Upravljačka ploča Plesk ima vrlo lijepu integraciju za Lets Encrypt. Lets Encrypt je jedan od jedinih SSL pružatelja usluga koji u potpunosti izdaju certifikate
Lets Encrypt je tijelo za izdavanje certifikata posvećeno besplatnom pružanju SSL certifikata. cPanel je izgradio urednu integraciju tako da vi i vaš klijent
Korištenje drugog sustava? Concrete5 je CMS otvorenog koda koji nudi mnoge osebujne i korisne značajke koje pomažu urednicima u jednostavnoj proizvodnji sadržaja i
Korištenje drugog sustava? Review Board je besplatan alat otvorenog koda za pregled izvornog koda, dokumentacije, slika i još mnogo toga. To je web-bazirani softver
U ovom vodiču naučit ćete kako postaviti HTTP autentifikaciju za Nginx web poslužitelj koji radi na CentOS 7. Zahtjevi Da biste započeli, trebat će vam
YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) je aplikacija za skraćivanje URL-ova otvorenog koda i analizu podataka. U ovom članku ćemo pokriti proces instalacije
Korištenje drugog sustava? Uvod ArangoDB je NoSQL baza podataka otvorenog koda s fleksibilnim modelom podataka za dokumente, grafikone i ključ-vrijednosti. to je
Uvod Direktorij /etc/ igra ključnu ulogu u načinu na koji Linux sustav funkcionira. Razlog tome je što je gotovo svaka konfiguracija sustava
Mnogi administratori sustava upravljaju velikim količinama poslužitelja. Kada se datotekama treba pristupiti na različitim poslužiteljima, prijava na svaki pojedinačno ca
Ovaj vodič će pokriti proces instaliranja poslužitelja za igre Half Life 2 na sustavu CentOS 6. Korak 1: Instaliranje preduvjeta Kako biste postavili ou
Laravel GitScrum ili GitScrum je alat za produktivnost otvorenog koda dizajniran da pomogne razvojnim timovima da implementiraju Scrum metodologiju na sličan način.
Umjetna inteligencija nije u budućnosti, ovdje je upravo u sadašnjosti. U ovom blogu Pročitajte kako su aplikacije umjetne inteligencije utjecale na različite sektore.
Jeste li i vi žrtva DDOS napada i zbunjeni ste metodama prevencije? Pročitajte ovaj članak kako biste riješili svoje upite.
Možda ste čuli da hakeri zarađuju mnogo novca, ali jeste li se ikada zapitali kako zarađuju toliki novac? raspravimo.
Želite li vidjeti revolucionarne izume Googlea i kako su ti izumi promijenili život svakog čovjeka danas? Zatim čitajte na blogu kako biste vidjeli Googleove izume.
Koncept samovozećih automobila koji će krenuti na ceste uz pomoć umjetne inteligencije san je koji već neko vrijeme imamo. No, unatoč nekoliko obećanja, nigdje ih nema. Pročitajte ovaj blog kako biste saznali više…
Kako se znanost razvija velikom brzinom, preuzimajući mnoge naše napore, raste i rizik da se podvrgnemo neobjašnjivoj Singularnosti. Pročitajte što bi za nas mogla značiti singularnost.
Metode pohrane podataka su se razvijale možda od rođenja podataka. Ovaj blog pokriva evoluciju pohrane podataka na temelju infografike.
Pročitajte blog kako biste na najjednostavniji način upoznali različite slojeve u arhitekturi velikih podataka i njihove funkcionalnosti.
U ovom digitalnom svijetu, pametni kućni uređaji postali su ključni dio života. Evo nekoliko nevjerojatnih prednosti pametnih kućnih uređaja o tome kako naš život čine vrijednim življenja i jednostavnijim.
Nedavno je Apple izdao macOS Catalina 10.15.4 dodatak ažuriranju kako bi riješio probleme, ali čini se da ažuriranje uzrokuje više problema koji dovode do zalijevanja mac strojeva. Pročitajte ovaj članak da biste saznali više