Εγκαταστήστε το Plesk στο CentOS 7
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Plesk είναι ένας ιδιόκτητος πίνακας ελέγχου web host που επιτρέπει στους χρήστες να διαχειρίζονται τους προσωπικούς ή/και τους πελάτες τους ιστότοπους, βάσεις δεδομένων
Ο H2O είναι ένας διακομιστής HTTP νέας γενιάς που διαθέτει εξαιρετικές, πλήρως εξοπλισμένες υλοποιήσεις HTTP/2 όλων των τρεχόντων διακομιστών Ιστού που χρησιμοποιούνται. Με τον H2O ως διακομιστή ιστού, μπορείτε να επωφεληθείτε από τις νέες δυνατότητες της προδιαγραφής HTTP/2, όπως η βελτιστοποίηση καθυστέρησης, η ώθηση διακομιστή και η ιεράρχηση από την πλευρά του διακομιστή που μπορούν να επωφεληθούν από τις σύγχρονες λειτουργίες του προγράμματος περιήγησης για τις οποίες σπάνια γίνεται λόγος.
Σε αυτό το λεπτομερές σεμινάριο, θα σας δείξω βήμα προς βήμα πώς να εκτελείτε το H2O στην παρουσία σας CentOS 7 x64.
Συνδεθείτε μέσω SSH με τα διαπιστευτήρια που βρίσκονται κάτω από την παρουσία σας και ενημερώστε το σύστημα ως εξής.
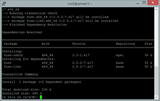
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum update -y
Για να εγκαταστήσετε το H2O στο CentOS 7, πρέπει να προσθέσετε το αποθετήριο Bintay RPM για να εγκαταστήσετε τα προκατασκευασμένα δυαδικά αρχεία H2O. Χρησιμοποιήστε το πρόγραμμα επεξεργασίας Nano για να δημιουργήσετε ένα προσαρμοσμένο αποθετήριο.
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/bintray-h2o-rpm.repo
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο αρχείο repo.
[bintray-h2o-rpm]
name=bintray-h2o-rpm
baseurl=https://dl.bintray.com/tatsushid/h2o-rpm/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Στη συνέχεια, εγκαταστήστε το H2O.
sudo yum install h2o -y
Τώρα που έχει εγκατασταθεί το H2O, αλλά προτού ενεργοποιήσετε και ξεκινήσετε την υπηρεσία, απαιτείται σωστή διαμόρφωση και πρέπει να δημιουργήσουμε έναν συγκεκριμένο χρήστη και ομάδα για την εκτέλεση του H2O. Δημιουργήστε μια ομάδα και έναν χρήστη για το H2O να εκτελείται με το όνομα h2o.
sudo groupadd -g 101 h2o
sudo useradd -d /etc/h2o -g 101 -M -s /sbin/nologin -u 101 h2o
Τα ακόλουθα βήματα θα δώσουν παραδείγματα ρυθμίσεων διαμόρφωσης για διάφορες ρυθμίσεις unencrypted, encrypted, staticκαι dynamicδιακομιστή. καθώς και συνδυασμός και των τεσσάρων.
http://www.example.comσε http://example.com(Στατικές σελίδες HTML, χωρίς PHP) ΔιαμόρφωσηΠλοηγηθείτε στον /etc/h2o/κατάλογο.
cd /etc/h2o/
Μετονομάστε την προεπιλογή h2o.confσε h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο h2o.confαρχείο.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο h2o.confαρχείο.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Ενεργοποιήστε και ξεκινήστε τον διακομιστή H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Δημιουργήστε μια προεπιλογή index.htmlχρησιμοποιώντας το πρότυπο στον /var/www/htmlκατάλογο που file.dirαναφέρεται παραπάνω στο /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Τώρα, ανοίξτε το πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας και εισαγάγετε το όνομα τομέα διακομιστή ( example.comή www.example.com) για την παράδειγμά σας. Λαμβάνετε Unable to connectένα This site can’t be reachedμήνυμα ή ένα μήνυμα; Η προεπιλεγμένη ρύθμιση τείχους προστασίας του CentOS δεν επιτρέπει τις εισερχόμενες συνδέσεις στη θύρα http. Εκτελέστε τα παρακάτω για να το ανοίξετε.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Ανανεώστε τη σελίδα στο πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας ( F5) και θα λάβετε αυτό το μήνυμα.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.comσε http://www.example.com(Στατικές σελίδες HTML, χωρίς PHP) ΔιαμόρφωσηΠλοηγηθείτε στον /etc/h2o/κατάλογο.
cd /etc/h2o/
Μετονομάστε την προεπιλογή h2o.confσε h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο h2o.confαρχείο.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο h2o.confαρχείο.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Ενεργοποιήστε και ξεκινήστε τον διακομιστή H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Δημιουργήστε ένα προεπιλεγμένο index.htmlαρχείο χρησιμοποιώντας το πρότυπο στην /var/www/htmlεπιλογή καταλόγου που file.dirαναφέρεται παραπάνω στο /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Τώρα, ανοίξτε το πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας και εισαγάγετε το όνομα τομέα διακομιστή ( example.comή www.example.com) για την παράδειγμά σας. Λαμβάνετε Unable to connectένα This site can’t be reachedμήνυμα ή ένα μήνυμα; Η προεπιλεγμένη ρύθμιση τείχους προστασίας του CentOS δεν επιτρέπει τις εισερχόμενες συνδέσεις στη θύρα http. Κάντε τα εξής για να το ανοίξετε.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Ανανεώστε τη σελίδα στο πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας ( F5) και θα λάβετε αυτό το μήνυμα.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://www.example.comσε http://example.com(Δυναμική σελίδα, PHP-FPM 5.6.x).Πλοηγηθείτε στον /etc/h2o/κατάλογο.
cd /etc/h2o/
Μετονομάστε την προεπιλογή h2o.confσε h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο h2o.confαρχείο.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο h2o.confαρχείο.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://www.example.com To http://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com To http://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "http://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text into the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Static HTML Pages, No PHP) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.html' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a default index.html using the template in /var/www/html to the directory option file.dir listed above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo cp -var /var/www/html /var/www/www.example.com
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get this message.
Welcome to H2O - an optimized HTTP server
It works!
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 5.6.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 5.6 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands to install PHP version 5.6.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php56-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/ directory.
cd /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-5.6-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-5.6.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /opt/remi/php56/root/var/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php56-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php56-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/www.example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://www.example.com to https://example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
In order to process PHP, the PHP-FPM 7.1 daemon must be installed and configured. In order to install a version of PHP-FPM newer than the default 5.4.x, the REMI repo must be installed which contains PHP versions 5.6.x, 7.0.x and 7.1.x. Type the following commands below to install PHP version 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Navigate to the /etc/opt/remi/php71/ directory.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Rename the default php-fpm.conf to php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Create a new php-fpm.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the php-fpm.conf file.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Rename the default www.conf file in the php-fpm.d directory.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Create a new www.conf file.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Copy and paste the following text into the www.conf file. Change your pm.max\_children to match the number of CPUs in accordance with your VPS instance.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Rename the default php.ini file.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Create a new php.ini file.
sudo nano php.ini
Copy and paste the following text below into the new php.ini file. Change the memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesize and date.timezone in accordance with your VPS instance.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Change the group ownership for the /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/ directory from the apache group to the h2o group.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Create a directory where the PHP-FPM server logs will reside.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Enable and start the PHP-FPM server.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Enable and start the H2O server.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Create a directory where the default index.php will reside listed by the directory option file.dir above in /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com
Create a default index.php using the phpinfo command to test PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.php
Copy and paste the text below in the new index.php file.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Now, open your browser and enter the server domain name (example.com or www.example.com) for your instance. Are you getting an Unable to connect or a This site can’t be reached message? CentOS's default firewall setting disallows incoming connections to the http port. Do the following to open it.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Refresh the page in your browser (F5) and you will get the standard PHP info page.
http://example.com, http://www.example.com, and https://example.com to https://www.example.com (Dynamic Page, PHP-FPM 7.1.x) ConfigurationNavigate to the /etc/h2o/ directory.
cd /etc/h2o/
Rename the default h2o.conf to h2o.conf.original.
sudo mv h2o.conf h2o.conf.original
Create a new h2o.conf file.
sudo nano h2o.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the h2o.conf file.
access-log: /var/log/h2o/access.log
compress: ON
error-log: /var/log/h2o/error.log
expires: 1 day
file.index: [ 'index.php' ]
hosts:
"example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://example.com/"
"www.example.com:80":
listen:
port: 80
paths:
"/":
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
status: 301
url: "https://www.example.com/"
"www.example.com:443":
listen:
port: 443
ssl:
<<: !file /etc/h2o/conf.d/ssl.conf
certificate-file: /location/of/certificate/file/fullchain.ext
key-file: /location/of/private/key/file/privkey.ext
paths:
"/":
file.dir: /var/www/www.example.com
header.add: "strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
redirect:
internal: YES
status: 307
url: /index.php
file.custom-handler:
extension: .php
fastcgi.connect:
port: /run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
type: unix
pid-file: /var/run/h2o/h2o.pid
send-server-name: OFF
setenv:
HTTP_PROXY: ""
user: h2o
Create a custom directory to store the default SSL options for all websites that use SSL.
sudo mkdir conf.d
Create a new ssl.conf file.
sudo nano conf.d/ssl.conf
Copy and paste the text below into the ssl.conf file.
cipher-preference: server
cipher-suite: ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
dh-file: /etc/ssl/h2o/dhparam_2048.pem
Make a directory to store the dhparam_2048.pem file that will be regenerated daily via a cronjob.
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/h2o/
Create a new regenerate_dhparam file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Copy and paste the following text inside of the regenerate_dhparam file.
#!/bin/bash
cd /etc/ssl/h2o
umask 022
for length in 2048
do
openssl dhparam -out dhparam_$length.tmp $length && mv dhparam_$length.tmp dhparam_$length.pem
chmod 444 dhparam_$length.pem
done
Make the bash file just created executable.
sudo chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Execute the bash script for a first run as H2O won't start properly if it's not generated. This will take about a minute or two to generate on first run.
sudo /etc/cron.daily/regenerate_dhparam
Για την επεξεργασία της PHP, πρέπει να εγκατασταθεί και να ρυθμιστεί ο δαίμονας PHP-FPM 7.1. Για να εγκαταστήσετε μια έκδοση του PHP-FPM νεότερη από την προεπιλεγμένη 5.4.x, πρέπει να εγκατασταθεί το αποθετήριο REMI που περιέχει τις εκδόσεις PHP 5.6.x, 7.0.x και 7.1.x. Πληκτρολογήστε τις ακόλουθες εντολές για να εγκαταστήσετε την έκδοση PHP 7.1.x.
sudo yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm -y
sudo yum install php71-php-fpm -y
Πλοηγηθείτε στον /etc/opt/remi/php71/κατάλογο.
cd /etc/opt/remi/php71/
Μετονομάστε την προεπιλογή php-fpm.confσε php-fpm.conf.original.
sudo mv php-fpm.conf php-fpm.conf.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο php-fpm.confαρχείο.
sudo nano php-fpm.conf
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο php-fpm.confαρχείο.
include=/etc/opt/remi/php71/php-fpm.d/*.conf
[global]
daemonize = yes
emergency_restart_threshold = 2
emergency_restart_interval = 1m
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm-7.1-error.log
pid = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.pid
process_control_timeout = 10s
Μετονομάστε το προεπιλεγμένο www.confαρχείο στον php-fpm.dκατάλογο.
sudo mv php-fpm.d/www.conf php-fpm.d/www.conf.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο www.confαρχείο.
sudo nano php-fpm.d/www.conf
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο www.confαρχείο. Αλλάξτε το pm.max\_childrenώστε να ταιριάζει με τον αριθμό των CPU σύμφωνα με το στιγμιότυπο VPS.
[www]
group = h2o
listen = /var/run/php-fpm-7.1.sock
listen.backlog = 65536
listen.owner = h2o
listen.group = h2o
pm = static
pm.max_children = 2
pm.max_requests = 10240
user = h2o
Μετονομάστε το προεπιλεγμένο php.iniαρχείο.
sudo mv php.ini php.ini.original
Δημιουργήστε ένα νέο php.iniαρχείο.
sudo nano php.ini
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο νέο php.ini file. Αλλαγή του memory\_limit, post\_max\_size, upload\_max\_filesizeκαι date.timezoneσύμφωνα με το παράδειγμα VPS σας.
[PHP]
allow_url_fopen = On
always_populate_raw_post_data = -1
display_errors = Off
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
expose_php = Off
log_errors = On
memory_limit = 256M
output_buffering = 4096
post_max_size = 64M
register_argc_argv = Off
request_order = "GP"
upload_max_filesize = 64M
variables_order = "GPCS"
[Date]
date.timezone = America/New_York
[Session]
session.cache_limiter =
session.gc_divisor = 1000
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
session.save_handler = files
session.save_path = "/var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session"
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
Αλλάξτε την ιδιοκτησία της ομάδας για τον /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/κατάλογο από την apacheομάδα στην h2oομάδα.
sudo chown root.h2o /var/opt/remi/php71/lib/php/session/
Δημιουργήστε έναν κατάλογο όπου θα βρίσκονται τα αρχεία καταγραφής διακομιστή PHP-FPM.
sudo mkdir /var/log/php-fpm/
Ενεργοποιήστε και ξεκινήστε τον διακομιστή PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl enable php71-php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php71-php-fpm
Ενεργοποιήστε και ξεκινήστε τον διακομιστή H2O.
sudo systemctl enable h2o
sudo systemctl start h2o
Δημιουργήστε έναν κατάλογο όπου η προεπιλογή index.phpθα παρατίθεται από την file.dirπαραπάνω επιλογή καταλόγου στο /var/www/example.com.
sudo mkdir /var/www/www.example.com
Δημιουργήστε μια προεπιλογή index.phpχρησιμοποιώντας την phpinfoεντολή για να δοκιμάσετε την PHP.
sudo nano /var/www/www.example.com/index.php
Αντιγράψτε και επικολλήστε το παρακάτω κείμενο στο νέο index.phpαρχείο.
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Τώρα, ανοίξτε το πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας και εισαγάγετε το όνομα τομέα διακομιστή ( example.comή www.example.com) για την παράδειγμά σας. Λαμβάνετε Unable to connectένα This site can’t be reachedμήνυμα ή ένα μήνυμα; Η προεπιλεγμένη ρύθμιση τείχους προστασίας του CentOS δεν επιτρέπει τις εισερχόμενες συνδέσεις στη θύρα http. Κάντε τα εξής για να το ανοίξετε.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Ανανεώστε τη σελίδα στο πρόγραμμα περιήγησής σας ( F5) και θα λάβετε την τυπική σελίδα πληροφοριών PHP.
Αυτό ολοκληρώνει το σεμινάριο μου. Ευχαριστώ για την ανάγνωση.
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Plesk είναι ένας ιδιόκτητος πίνακας ελέγχου web host που επιτρέπει στους χρήστες να διαχειρίζονται τους προσωπικούς ή/και τους πελάτες τους ιστότοπους, βάσεις δεδομένων
Το Squid είναι ένα δημοφιλές, δωρεάν πρόγραμμα Linux που σας επιτρέπει να δημιουργήσετε έναν διακομιστή μεσολάβησης web προώθησης. Σε αυτόν τον οδηγό, θα δείτε πώς να εγκαταστήσετε το Squid στο CentOS για να σας μετατρέψει
Εισαγωγή Το Lighttpd είναι ένα πιρούνι του Apache που έχει ως στόχο να είναι πολύ λιγότερο εντάσεως πόρων. Είναι ελαφρύ, εξ ου και το όνομά του, και είναι αρκετά απλό στη χρήση. Εγκατάσταση
Το Icinga2 είναι ένα ισχυρό σύστημα παρακολούθησης και όταν χρησιμοποιείται σε μοντέλο master-client, μπορεί να αντικαταστήσει την ανάγκη για ελέγχους παρακολούθησης που βασίζονται σε NRPE. Ο κύριος-πελάτης
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Apache Cassandra είναι ένα δωρεάν και ανοιχτού κώδικα σύστημα διαχείρισης βάσεων δεδομένων NoSQL που έχει σχεδιαστεί για να παρέχει επεκτασιμότητα, υψηλή
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Microweber είναι ένα ανοικτού κώδικα μεταφοράς και απόθεσης CMS και ηλεκτρονικό κατάστημα. Ο πηγαίος κώδικας Microweber φιλοξενείται στο GitHub. Αυτός ο οδηγός θα σας δείξει
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Vanilla forum είναι μια εφαρμογή φόρουμ ανοιχτού κώδικα γραμμένη σε PHP. Είναι πλήρως προσαρμόσιμο, εύκολο στη χρήση και υποστηρίζει εξωτερικά
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Mattermost είναι μια εναλλακτική λύση ανοιχτού κώδικα, που φιλοξενείται από τον εαυτό της στην υπηρεσία ανταλλαγής μηνυμάτων Slack SAAS. Με άλλα λόγια, με το Mattermost, μπορείτε περίπου
Ο πίνακας ελέγχου Plesk διαθέτει μια πολύ ωραία ενσωμάτωση για το Lets Encrypt. Το Lets Encrypt είναι ένας από τους μόνους παρόχους SSL που εκδίδει πιστοποιητικά πλήρως
Το Lets Encrypt είναι μια αρχή έκδοσης πιστοποιητικών αφιερωμένη στην παροχή πιστοποιητικών SSL δωρεάν. Το cPanel έχει δημιουργήσει μια τακτοποιημένη ενοποίηση για εσάς και τον πελάτη σας
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Concrete5 είναι ένα CMS ανοιχτού κώδικα που προσφέρει πολλές χαρακτηριστικές και χρήσιμες λειτουργίες για να βοηθήσει τους συντάκτες να παράγουν περιεχόμενο εύκολα και
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Το Review Board είναι ένα δωρεάν και ανοιχτού κώδικα εργαλείο για την ανασκόπηση του πηγαίου κώδικα, της τεκμηρίωσης, των εικόνων και πολλών άλλων. Είναι λογισμικό που βασίζεται στο web
Σε αυτόν τον οδηγό, θα μάθετε πώς να ρυθμίζετε τον έλεγχο ταυτότητας HTTP για έναν διακομιστή web Nginx που εκτελείται σε CentOS 7. Απαιτήσεις Για να ξεκινήσετε, θα χρειαστείτε
Το YOURLS (Your Own URL Shortener) είναι μια εφαρμογή συντόμευσης διευθύνσεων URL και ανάλυσης δεδομένων ανοιχτού κώδικα. Σε αυτό το άρθρο, θα καλύψουμε τη διαδικασία εγκατάστασης
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα διαφορετικό σύστημα; Εισαγωγή Το ArangoDB είναι μια βάση δεδομένων NoSQL ανοιχτού κώδικα με ένα ευέλικτο μοντέλο δεδομένων για έγγραφα, γραφήματα και κλειδιά-τιμές. είναι
Εισαγωγή Ο κατάλογος /etc/ παίζει κρίσιμο ρόλο στον τρόπο λειτουργίας ενός συστήματος Linux. Ο λόγος για αυτό είναι επειδή σχεδόν κάθε διαμόρφωση συστήματος
Πολλοί διαχειριστές συστημάτων διαχειρίζονται μεγάλες ποσότητες διακομιστών. Όταν χρειάζεται πρόσβαση στα αρχεία σε διαφορετικούς διακομιστές, συνδέεστε σε καθένα ξεχωριστά περίπου
Αυτό το σεμινάριο θα καλύψει τη διαδικασία εγκατάστασης ενός διακομιστή παιχνιδιών Half Life 2 στο σύστημα CentOS 6. Βήμα 1: Εγκατάσταση των προαπαιτούμενων Για να ρυθμίσετε το ou
Το Laravel GitScrum ή GitScrum είναι ένα εργαλείο παραγωγικότητας ανοιχτού κώδικα που έχει σχεδιαστεί για να βοηθά τις ομάδες ανάπτυξης να εφαρμόσουν τη μεθοδολογία Scrum με παρόμοιο τρόπο
Εισαγωγή Σε αυτό το σεμινάριο Vultr, θα μάθετε πώς να εγκαταστήσετε το PowerDNS. Το PowerDNS είναι ένα πρόγραμμα για την εκτέλεση των δικών σας διακομιστών ονομάτων. Είναι πολύ χρήσιμο όταν
Η Τεχνητή Νοημοσύνη δεν είναι στο μέλλον, είναι εδώ ακριβώς στο παρόν Σε αυτό το blog Διαβάστε πώς οι εφαρμογές Τεχνητής Νοημοσύνης έχουν επηρεάσει διάφορους τομείς.
Είστε επίσης θύμα των επιθέσεων DDOS και έχετε μπερδευτεί σχετικά με τις μεθόδους πρόληψης; Διαβάστε αυτό το άρθρο για να λύσετε τις απορίες σας.
Μπορεί να έχετε ακούσει ότι οι χάκερ κερδίζουν πολλά χρήματα, αλλά έχετε αναρωτηθεί ποτέ πώς κερδίζουν τέτοια χρήματα; ας συζητήσουμε.
Θέλετε να δείτε επαναστατικές εφευρέσεις της Google και πώς αυτές οι εφευρέσεις άλλαξαν τη ζωή κάθε ανθρώπου σήμερα; Στη συνέχεια, διαβάστε στο blog για να δείτε τις εφευρέσεις της Google.
Η ιδέα των αυτοκινούμενων αυτοκινήτων να βγαίνουν στους δρόμους με τη βοήθεια της τεχνητής νοημοσύνης είναι ένα όνειρο που έχουμε εδώ και καιρό. Όμως, παρά τις πολλές υποσχέσεις, δεν φαίνονται πουθενά. Διαβάστε αυτό το blog για να μάθετε περισσότερα…
Καθώς η Επιστήμη εξελίσσεται με γρήγορους ρυθμούς, αναλαμβάνοντας πολλές από τις προσπάθειές μας, αυξάνονται και οι κίνδυνοι να υποβάλλουμε τον εαυτό μας σε μια ανεξήγητη Ιδιότητα. Διαβάστε τι σημαίνει η μοναδικότητα για εμάς.
Οι μέθοδοι αποθήκευσης των δεδομένων εξελίσσονται μπορεί να είναι από τη γέννηση των Δεδομένων. Αυτό το ιστολόγιο καλύπτει την εξέλιξη της αποθήκευσης δεδομένων με βάση ένα infographic.
Διαβάστε το ιστολόγιο για να μάθετε διαφορετικά επίπεδα στην Αρχιτεκτονική Μεγάλων Δεδομένων και τις λειτουργίες τους με τον απλούστερο τρόπο.
Σε αυτόν τον ψηφιακό κόσμο, οι έξυπνες οικιακές συσκευές έχουν γίνει κρίσιμο μέρος της ζωής. Ακολουθούν μερικά εκπληκτικά οφέλη των έξυπνων οικιακών συσκευών σχετικά με το πώς κάνουν τη ζωή μας να αξίζει και να απλοποιείται.
Πρόσφατα, η Apple κυκλοφόρησε το macOS Catalina 10.15.4 μια συμπληρωματική ενημέρωση για την επιδιόρθωση προβλημάτων, αλλά φαίνεται ότι η ενημέρωση προκαλεί περισσότερα προβλήματα που οδηγούν σε bricking των μηχανών mac. Διαβάστε αυτό το άρθρο για να μάθετε περισσότερα