Install Plesk on CentOS 7
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
Graylog server is an enterprise ready open source log management software suite. It collects logs from various sources and analyses them to discover and resolve issues. Greylog server is basically the combination of Elasticsearch, MongoDB and Graylog. Elasticsearch is a very popular open source application to store text and provide very powerful search capabilities. MongoDB is an open source application to store data in NoSQL format. Graylog collects logs from various sources and provides a web-based dashboard to manage and search through the logs. Graylog also provides a REST API for both configuration and data. It provides a configurable dashboard which can be used to visualize metrics and observe trends by using field statistics, quick values, and charts from one central location.
In this tutorial, you will learn to install Graylog Server on Ubuntu 16.04. This guide was written for Graylog Server 2.3, but may work on newer versions as well. You will also learn to install Java, Elasticsearch and MongoDB. We will also secure the MongoDB instance and set up an Nginx reverse proxy for the web-based dashboard and API.
In this tutorial, we will use 192.0.2.1 as the public IP address of the server and graylog.example.com as the domain name pointed to the server. Replace all occurrences of 192.0.2.1 with your Vultr public IP address and graylog.example.com with your actual domain name.
Update your base system using the guide How to Update Ubuntu 16.04. Once your system has been updated, proceed to install Java.
Elasticsearch requires Java 8 to run. It supports both Oracle Java and OpenJDK, but it is always recommended that you use Oracle Java when possible. Add Oracle Java PPA repository:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
Update the APT repository metadata:
sudo apt update
Install the latest stable version of Java 8, run:
sudo apt -y install oracle-java8-installer
Accept the licence agreement when prompted. If Java has installed successfully, then you should be able to verify its version.
java -version
You will see the following output.
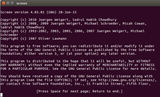
user@vultr:~$ java -version
java version "1.8.0_144"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_144-b01)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.144-b01, mixed mode)
Set the JAVA_HOME and other defaults by installing oracle-java8-set-default. Run:
sudo apt -y install oracle-java8-set-default
Run the echo $JAVA_HOME command to check if the environment variable is set or not.
user@vultr:~$ echo "$JAVA_HOME"
/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle
If you do not get the output shown above, you may need to logout and login to the shell again.
Elasticsearch is a distributed, real time, scalable and highly available application used to store the logs and search through them. It stores the data in indexes and searching through the data is very fast. It provides various sets of APIs, such as HTTP RESTful API and native Java API. Elasticsearch can be installed directly through the Elasticsearch repository. Add the Elasticsearch APT repository:
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/5.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-5.x.list
Import the PGP key used to sign the packages. This will ensure the integrity of the packages.
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
Update the APT repository metadata.
sudo apt update
Install the Elasticsearch package:
sudo apt -y install elasticsearch
Once the package is installed, open the Elasticsearch default configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Find the following line, uncomment it and change the value from my-application to graylog.
cluster.name: graylog
You can start Elasticsearch and enable it to automatically start at boot time:
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is now running on port 9200. Verify that it is working properly by running:
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
You should see output similar to the following.
[user@vultr ~]$ curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
{
"name" : "-kYzFA9",
"cluster_name" : "graylog",
"cluster_uuid" : "T3JQKehzSqmLThlVkEKPKg",
"version" : {
"number" : "5.5.1",
"build_hash" : "19c13d0",
"build_date" : "2017-07-18T20:44:24.823Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "6.6.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
If you encounter errors, wait for a few seconds and retry, as it takes time for Elasticsearch to complete its start-up process. Elasticsearch is now installed and working correctly.
MongoDB is free and open source NoSQL database server. Unlike traditional database which uses tables to organize their data, MongoDB is document-oriented and uses JSON-like documents without schemas. Graylog uses MongoDB to store its configuration and meta information. It can be installed directly through the MongoDB repository. Import the GPG key used to sign the package. This will ensure the authenticity of the packages.
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 0C49F3730359A14518585931BC711F9BA15703C6
Now create the Repository file:
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/3.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.list
Update the APT repository metadata.
sudo apt update
Install MongoDB package:
sudo apt -y install mongodb-org
Start MongoDB server and enable it to start automatically.
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongod
Download and the latest repository for Graylog server.
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-2.3-repository_latest.deb
sudo dpkg -i graylog-2.3-repository_latest.deb
sudo apt update
Install Graylog package:
sudo apt install graylog-server
Graylog server is now installed on your server. Before you can start it, you will need to configure a few things.
Install pwgen utility to generate strong passwords.
sudo apt -y install pwgen
Now generate a strong password secret.
pwgen -N 1 -s 96
You will output similar to:
[user@vultr ~]$ pwgen -N 1 -s 96
pJqhNbdEY9FtNBfFUtq20lG2m9daacmsZQr59FhyoA0Wu3XQyVZcu5FedPZ9eCiDfjdiYWfRcEQ7a36bVqxSyTzcMMx5Rz8v
Also, generate a 256-bit hash for the password of the root admin user:
echo -n StrongPassword | sha256sum
Replace StrongPassword with the password you wish to set for admin user. You will see:
[user@vultr ~]$ echo -n StrongPassword | sha256sum
05a181f00c157f70413d33701778a6ee7d2747ac18b9c0fbb8bd71a62dd7a223 -
Open the Graylog configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Find password_secret =, copy and paste the password generated through pwgen command. Find root_password_sha2 =, copy and paste the converted SHA 256-bit hash of your admin password. Find #root_email =, uncomment and provide your email address. Uncomment and set your time zone at root_timezone. For example:
password_secret = pJqhNbdEY9FtNBfFUtq20lG2m9daacmsZQr59FhyoA0Wu3XQyVZcu5FedPZ9eCiDfjdiYWfRcEQ7a36bVqxSyTzcMMx5Rz8v
root_password_sha2 = 05a181f00c157f70413d33701778a6ee7d2747ac18b9c0fbb8bd71a62dd7a223
root_email = [email protected]
root_timezone = Asia/Kolkata
Enable the web-based Graylog interface by uncommenting #web_enable = false and setting its value to true. Also uncomment and change the following lines as specified.
rest_listen_uri = http://0.0.0.0:9000/api/
rest_transport_uri = http://192.0.2.1:9000/api/
web_enable = true
web_listen_uri = http://0.0.0.0:9000/
Save the file and exit from your text editor.
Restart and enable the Graylog service by running:
sudo systemctl restart graylog-server
sudo systemctl enable graylog-server
By default, the Graylog web interface listens to localhost on port 9000 and the API listens on port 9000 with URL /api. In this tutorial, we will use Nginx as the reverse proxy so that the application can be access via standard HTTP port. Install Nginx web server by running:
sudo apt -y install nginx
Open the default virtual host file by typing.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Replace the existing content with the following lines:
server
{
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server ipv6only=on;
server_name 192.0.2.1 graylog.example.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Graylog-Server-URL http://$server_name/api;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9000;
}
}
Start Nginx and enable it to start automatically at boot time:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
The installation and basic configuration of Graylog server is now complete. You can now access the Graylog server on http://192.0.2.1 or http://graylog.example.com if you have DNS configured. Login using the username admin and the plain text version of the password you have set for root_password_sha2 earlier.
Congratulations - you have a fully working Graylog server installed on your Ubuntu 16.04 server.
Using a Different System? Plesk is a proprietary web host control panel that allows users to administer their personal and/or clients websites, databases
Introduction Lets Encrypt is a certificate authority service that offers free TLS/SSL certificates. The process of installation is simplified by Certbot,
Používate iný systém? Čo je Tekkit Classic? Tekkit Classic je modpack pre hru, ktorú každý pozná a miluje; Minecraft. Obsahuje niektoré z ver
Using a Different System? Jekyll is a great alternative to WordPress for blogging or sharing content. It doesnt require any databases and it is very easy i
Používate iný systém? Ak si zakúpite server Debian, mali by ste mať vždy najnovšie bezpečnostné záplaty a aktualizácie, či už spíte alebo nie
PHP a súvisiace balíky sú najčastejšie používané komponenty pri nasadzovaní webového servera. V tomto článku sa naučíme, ako nastaviť PHP 7.0 alebo PHP 7.1 o
Squid je populárny bezplatný linuxový program, ktorý vám umožňuje vytvoriť webový proxy server na presmerovanie. V tejto príručke uvidíte, ako nainštalovať Squid na CentOS, aby vás zmenil
Úvod Lighttpd je fork Apache, ktorého cieľom je byť oveľa menej náročný na zdroje. Je ľahký, odtiaľ jeho názov, a jeho použitie je celkom jednoduché. Installin
1. Virtualmin/Webmin Virtualmin je výkonný a flexibilný ovládací panel webhostingu pre systémy Linux a UNIX založený na známej webovej základni Open Source
Yii je rámec PHP, ktorý vám umožňuje rýchlejšie a jednoduchšie vyvíjať aplikácie. Inštalácia Yii na Ubuntu je jednoduchá, ako sa presne dozviete
Screen je aplikácia, ktorá umožňuje viacnásobné použitie terminálových relácií v rámci jedného okna. To vám umožňuje simulovať viacero okien terminálu, kde je to možné
Tento tutoriál vysvetľuje, ako nastaviť server DNS pomocou Bind9 na Debiane alebo Ubuntu. V celom článku podľa toho nahraďte názov vašej-domény.com. Pri th
Úvod Logrotate je nástroj pre Linux, ktorý zjednodušuje správu protokolových súborov. Zvyčajne beží raz denne prostredníctvom úlohy cron a spravuje základňu protokolov
VULTR nedávno vykonal zmeny na ich konci a všetko by teraz malo fungovať dobre po vybalení so zapnutým NetworkManagerom. Ak chcete deaktivovať
Icinga2 je výkonný monitorovací systém a pri použití v modeli master-client môže nahradiť potrebu monitorovacích kontrol založených na NRPE. Hlavný klient
Používate iný systém? Red5 je mediálny server s otvoreným zdrojom implementovaný v jazyku Java, ktorý vám umožňuje spúšťať aplikácie Flash pre viacerých používateľov, ako napríklad živé vysielanie
Používate iný systém? Apache Cassandra je bezplatný a otvorený systém správy databáz NoSQL, ktorý je navrhnutý tak, aby poskytoval škálovateľnosť, vysokú
Používate iný systém? Vanilla forum je open source aplikácia fóra napísaná v PHP. Je plne prispôsobiteľný, ľahko použiteľný a podporuje externé
Používate iný systém? Úvod Kanboard je bezplatný a otvorený softvérový program na riadenie projektov, ktorý je navrhnutý tak, aby uľahčil a vizualizoval
Používate iný systém? Úvod Kanboard je bezplatný a otvorený softvérový program na riadenie projektov, ktorý je navrhnutý tak, aby uľahčil a vizualizoval
Umelá inteligencia nie je v budúcnosti, je tu priamo v súčasnosti V tomto blogu si prečítajte, ako aplikácie umelej inteligencie ovplyvnili rôzne sektory.
Ste aj vy obeťou DDOS útokov a máte zmätok ohľadom metód prevencie? Ak chcete vyriešiť svoje otázky, prečítajte si tento článok.
Možno ste už počuli, že hackeri zarábajú veľa peňazí, ale premýšľali ste niekedy nad tým, ako môžu zarábať také peniaze? poďme diskutovať.
Chcete vidieť revolučné vynálezy od Google a ako tieto vynálezy zmenili život každého dnešného človeka? Potom si prečítajte na blogu a pozrite si vynálezy spoločnosti Google.
Koncept samoriadených áut vyraziť na cesty s pomocou umelej inteligencie je snom, ktorý máme už nejaký čas. Ale napriek niekoľkým prísľubom ich nikde nevidno. Prečítajte si tento blog a dozviete sa viac…
Ako sa veda vyvíja rýchlym tempom a preberá veľa nášho úsilia, zvyšuje sa aj riziko, že sa vystavíme nevysvetliteľnej singularite. Prečítajte si, čo pre nás môže znamenať singularita.
Spôsoby ukladania údajov sa môžu vyvíjať už od zrodu údajov. Tento blog sa zaoberá vývojom ukladania údajov na základe infografiky.
Prečítajte si blog, aby ste čo najjednoduchším spôsobom spoznali rôzne vrstvy architektúry veľkých dát a ich funkcie.
V tomto digitálnom svete sa inteligentné domáce zariadenia stali kľúčovou súčasťou života. Tu je niekoľko úžasných výhod inteligentných domácich zariadení o tom, ako robia náš život, ktorý stojí za to žiť, a ktorý zjednodušujú.
Spoločnosť Apple nedávno vydala doplnkovú aktualizáciu macOS Catalina 10.15.4 na opravu problémov, ale zdá sa, že táto aktualizácia spôsobuje ďalšie problémy, ktoré vedú k blokovaniu počítačov Mac. Prečítajte si tento článok a dozviete sa viac